TimedCache 带时间缓存工具类,附加监听回调 | Java工具类
简述
我们在工作中会碰到需要使用带过期时间的缓存场景。但是使用redis有太重了,毕竟缓存的数据很小,放在内存够够的。hutools提供了TimedCache时间缓存工具,可以实现该场景。下面使用到该组件,并为了适配工作场景,对该工具类做优化升级。
Maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.4.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>30.1.1-jre</version>
</dependency>
简单使用
不多说了,上代码。
import cn.hutool.cache.CacheUtil;
import cn.hutool.cache.impl.TimedCache;
import cn.hutool.core.thread.ThreadUtil;
/** @Author huyi @Date 2021/10/12 17:00 @Description: */
public class TimedCacheUtils {
private static final TimedCache<String, String> TIMED_CACHE = CacheUtil.newTimedCache(5000);
static {
/** 每5ms检查一次过期 */
TIMED_CACHE.schedulePrune(5);
}
/**
* 存入键值对,提供消逝时间
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @param timeout
*/
public static void put(String key, String value, Long timeout) {
/** 设置消逝时间 */
TIMED_CACHE.put(key, value, timeout);
}
/**
* 每次重新get一次缓存,均会重新刷新消逝时间
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static String get(String key) {
return TIMED_CACHE.get(key);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
put("haha", "1", 3000L);
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
// if (TIMED_CACHE.containsKey("haha")) {
// System.out.println("aa");
// }
System.out.println("第1次结果:" + get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("第2次结果:" + get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("第3次结果:" + get("haha"));
// 取消定时清理
TIMED_CACHE.cancelPruneSchedule();
}
}
首先我们看一下执行的效果
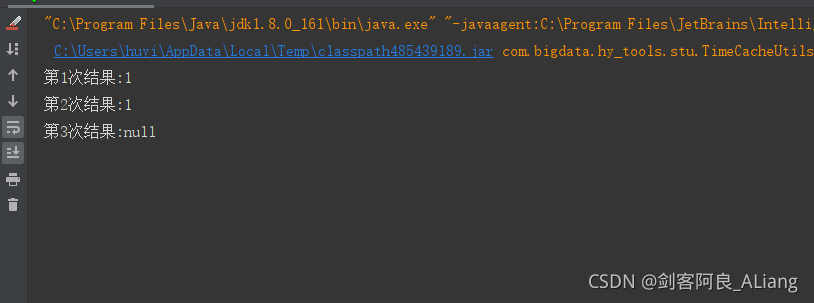
** 说明:**
1、设置的超时时间为3000毫秒,所以第一次打印在2秒钟,所以可以获取到值。
2、因为第一次打印调用了get方法,刷新了过期时间,所以依然可以获取到值。
3、第三次打印在5秒后,所以已经过期,无法获取到值,打印null。
那么,需要知道是否缓存还在可以使用containsKey方法。如下:
put("haha", "1", 3000L);
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
if (TIMED_CACHE.containsKey("haha")) {
System.out.println("第1次结果:缓存存在");
}
// System.out.println("第1次结果:" + get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("第2次结果:" + get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("第3次结果:" + get("haha"));
// 取消定时清理
TIMED_CACHE.cancelPruneSchedule();
工具优化-监听过期、增加回调
我们在使用TimedCache会发现,一旦缓存过期我们并不能立马知道,很多工作场景中需要对缓存做监听回调。所以我升级了一下该工具类。
import cn.hutool.cache.CacheUtil;
import cn.hutool.cache.impl.TimedCache;
import cn.hutool.core.thread.ThreadUtil;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.*;
import org.checkerframework.checker.nullness.qual.Nullable;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
/** @Author 剑客阿良_ALiang @Date 2021/10/12 10:57 @Description: 时间缓存工具 */
public class TimedCacheUtils {
private static final TimedCache<String, String> TIMED_CACHE = CacheUtil.newTimedCache(5000);
/** 线程池 */
private static final ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
private static final ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService =
MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(executorService);
/** 回调方法映射 */
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Consumer<String>> callbackMap;
/**
* 存入键值对,添加过期时间,和消费回调
*
* @param key
* @param timeout
* @param consumer
*/
public static void put(String key, String value, Long timeout, Consumer<String> consumer) {
TIMED_CACHE.put(key, value, timeout);
addListen(key, consumer);
}
/**
* 获取缓存值
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static String get(String key) {
return TIMED_CACHE.get(key);
}
/**
* 删除缓存和回调映射
*
* @param key
*/
public static void remove(String key) {
callbackMap.remove(key);
TIMED_CACHE.remove(key);
}
/**
* 添加监听器
*
* @param key
* @param consumer
*/
public static void addListen(String key, Consumer<String> consumer) {
ListenableFuture<String> listenableFuture =
listeningExecutorService.submit(
() -> {
while (TIMED_CACHE.containsKey(key)) {
ThreadUtil.sleep(500);
}
return key;
});
Futures.addCallback(
listenableFuture,
new FutureCallback<String>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(@Nullable String s) {
consumer.accept(s);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
},
listeningExecutorService);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
put("haha", "1", 3000L, x -> System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("[{0}] - 缓存消逝", x)));
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(get("haha"));
ThreadUtil.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(get("haha"));
// 关闭监听线程池
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
}
}
** 执行结果:**
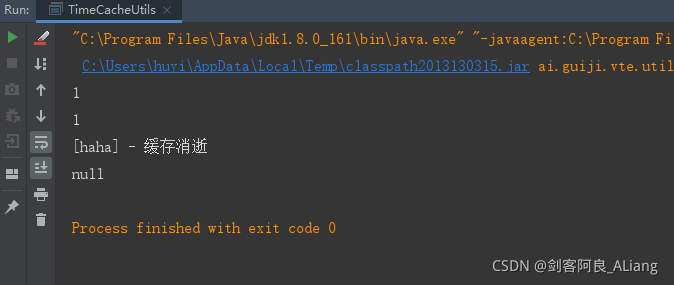
** 说明:**
1、可以看到监听到缓存过期,并进行了回调。
总结
具体的工具类使用场景,因项目而异,大家看着来。
如果本文对你有帮助,请点个赞支持一下吧。

本人CSDN主页地址:剑客阿良_ALiang的主页
一起学习,一起进步。
