Java-SpringBoot实现AOP (@Around)
AOP基本总结
-
连接点(JoinPoint):
- 连接点是程序运行的某个阶段点,如方法调用、异常抛出等
-
切入点(Pointcut):
- 切入点是JoinPoint的集合
- 是程序中需要注入Advice的位置的集合,即Advice在什么条件下才能被触发
-
增强(Advisor):
- 增强是切入点Pointcut和Advice的综合体,即在连接点JoinPoint上执行的行为
- 通过JDK/CGLIB代理模式实现AOP
-
切面(Aspect):
- @Aspect通常是一个类的注解,通常与@Component搭配使用
-
AOP代理(AOP Proxy):
- AOP使用动态代理模式创建对象,从而实现在连接点JoinPoint处插入增强
- 其中JDK只能代理接口,CGLIB基于子类但不能代理final类
常用方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
| Object[] getArgs | 返回目标方法的参数数组 |
| Signature getSignature | 返回目标方法所在类信息 |
| Object getTarget | 返回被织入增强处理的目标对象 |
| Object getThis |
返回AOP代理对象 |
| Object proceed(Object[] args) |
利用反射执行目标方法并返回结果 |
增强类型
-
@Before:前置增强,在某个JoinPoint执行前的增强
-
@After:final增强,不管抛异常还是正常退出都执行的增强
-
@AfterReturning:后置增强,方法正常退出时执行
-
@AfterThrowing:异常抛出增强,抛出异常后执行
-
@Around:环绕增强,包围一个连接点的增强,最强大的一个方式,且常用
示例说明
学了一下AOP的使用,写了个@Around的demo,将几个查询操作存入数据库作为Log并且定时清理过期数据
本人的Demo用的是Dubbo框架,而AOP的示例写在了Provider中,大概结构如下:
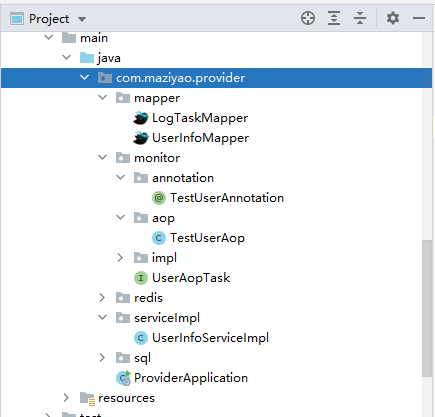
- monitor:
- annotation:注解类
- aop:切面的定义及实现
- impl:UserAopTask接口的实现类
1)UserLog实体类
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class UserLog implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String methodName;
private String methodArgs;
private String classFullName;
private String className;
private Date invokeTime;
private Double costTime;
}
2)LogTaskMapper对应mapper接口
public interface LogTaskMapper {
/**
* TEST AOP INSERT INFO INTO TABLE
* @param userLog
*/
void insertUserLog(UserLog userLog);
/**
* DELETE LOGS IN TABLE LAST x MINUTES
* @param minutes
*/
void deleteUserLog(int minutes);
}
3)UserAopTask接口
public interface UserAopTask {
void insertUserLog(UserLog log);
}
4)UserAopTaskImpl实现类
@Component
public class UserAopTaskImpl implements UserAopTask {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserAopTask.class);
@Autowired
private LogTaskMapper logTaskMapper;
private ExecutorService logHandler = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);//采用线程池复用一个线程执行
private static final int MINUTES_LOG_RETAIN = 30;//数据库中数据保留时间
@Override
public void insertUserLog(UserLog log) {
logHandler.submit(new logSubmitTask(log));
}
//内部类
class logSubmitTask implements Runnable{
private UserLog userLog;
public logSubmitTask(UserLog userLog){
this.userLog = userLog;
}
@Override
public void run() {
logTaskMapper.insertUserLog(userLog);
}
}
//定时清理任务
@Scheduled(cron = "0 30 * * * *")
public void scheduledDeleteLog(){
logger.info("开始清除[{}]分钟之前的图表查询日志...", MINUTES_LOG_RETAIN);
logTaskMapper.deleteUserLog(-1 * MINUTES_LOG_RETAIN);
}
}
5)TestUserAop切面类
@Aspect//切面
@Component//Spring容器管理
public class TestUserAop {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TestUserAop.class);
@Autowired
private UserAopTask userAopTask;
//使用环绕增强,第一参数必须是ProceedingJoinPoint
@Around(value = "@annotation(annotation)")//和注解类参数名保持一致
public Object aroundUserInfo(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, TestUserAnnotation annotation) throws Throwable{
UserLog userLog = new UserLog();
System.out.println("=====================ANNOTATION BEGIN=====================");
Date date = new Date();
Long methodStart = date.getTime();//timestamp
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 开始耗时统计: "+ date);
userLog.setInvokeTime(date);
Object[] argsObj = pjp.getArgs();
Object res = pjp.proceed(argsObj);//利用反射调用目标方法
Long methodCost = System.currentTimeMillis() - methodStart;
double cost = methodCost/1000d;//timestamp 转换为 seconds
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用方法总耗时: "+ String.format("%.3f",cost) +" s");//保留3位小数
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用方法: "+annotation.methodName());//目标方法
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用方法参数: "+ new Integer((Integer) argsObj[0]));//我的参数就1个或者无参
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用类: "+pjp.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());//全类名
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用类名: "+pjp.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName());//类名
System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用结果: "+ JSON.toJSON(res));
System.out.println("=====================ANNOTATION FINISHED=====================");
userLog.setCostTime(Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.3f",cost)));
userLog.setClassFullName(pjp.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
userLog.setClassName(pjp.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName());
userLog.setMethodName(annotation.methodName());
userLog.setMethodArgs(Integer.toString(new Integer((Integer) argsObj[0])));
userAopTask.insertUserLog(userLog);
return res;
}
}
6)TestUserAnnotation注解类
我在service层写的AOP demo,对目标方法使用注解,注解名为注解类名即可,如@TestUserAnnotation
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//运行时有效
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//作用于方法
@Documented
public @interface TestUserAnnotation {
String methodName() default "";//方法名,默认为空字符串
}
7)LogTaskMapper.xml
最后贴个代码,为上面提到的定时任务,用到的是date_add()方法,其中的 “<” 意为 “<“
<delete id="deleteUserLog" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from invoke_log
where invoke_time < date_add(current_timestamp,interval #{minutes} minute)
</delete>
结果展示
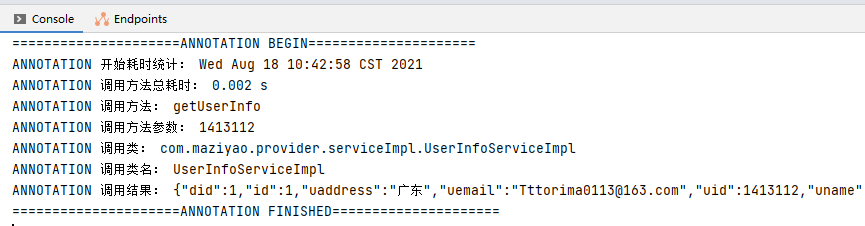
演示一下AOP的效果,将@TestUserAnnotation注解在方法getUserInfo(),即获取用户信息
Demo中利用AOP的@Around环绕增强,实现了统计方法调用运行消耗时间,以及统计调用方法名、类名等信息:

调用方法getUserInfo后的统计结果: