ssm-mybatis进阶之复杂结果集映射
ssm-mybatis进阶之复杂结果集映射
一、简单映射
先准备好数据库和工程,准备工作可以参考之前的记录。下面举例简单说明将数据库中查询的数据映射为对象是如何实现的:
- mapper中编写方法:
- 映射文件中写查询:
- 编写测试代码:
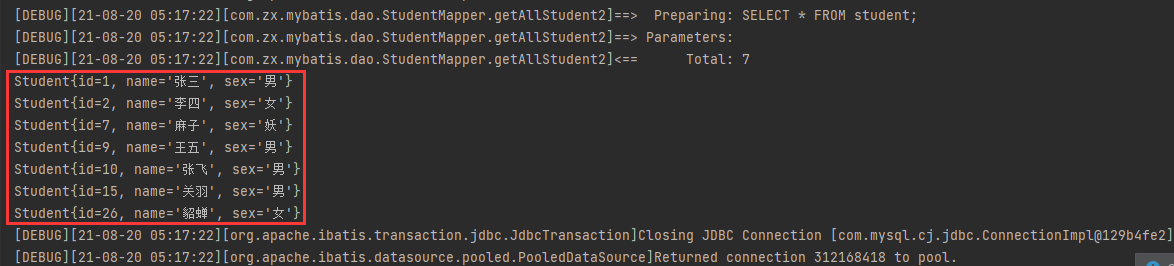
- 运行查看结果:
List<Student> getAllStudent2();
<select id="getAllStudent2" resultType="com.zx.mybatis.pojo.Student">
SELECT *
FROM student;
</select>
@Test
public void getAllStudent2() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
for (Student student : mapper.getAllStudent2()) {
System.out.println(student);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
除了映射为pojo,还能映射到map中,具体可以看之前的几篇记录。
二、复杂结果映射简介
实际开发中除了这种只有简单基础类型的对象外,还会遇到一些复杂的情况,如在返回结果映射对象中包含内部类,这种情况在映射中主要分为一对一和一对多。
业务开发中,会将这类复杂对象转换为复杂的嵌套json返回给客户端。
- 一对一型:包含内部类
public class StudentAndClass {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Class cls;
}public class ClassStudent {
private String cid;
private String cname;
private List<Student> students;
}三、一对一型映射
这类对象特征是pojo中包含内部类。
- mapper中编写方法:
- 映射文件中写查询:
- 编写测试代码:
- 运行查看结果:
- pom.xml中引用fastjson依赖,将数据转换为json输出:
List<StudentAndClass> getStudentAndClassBySex2(String s);
这里的查询相比上面的简单查询来说就比较复杂了,先看个实例:
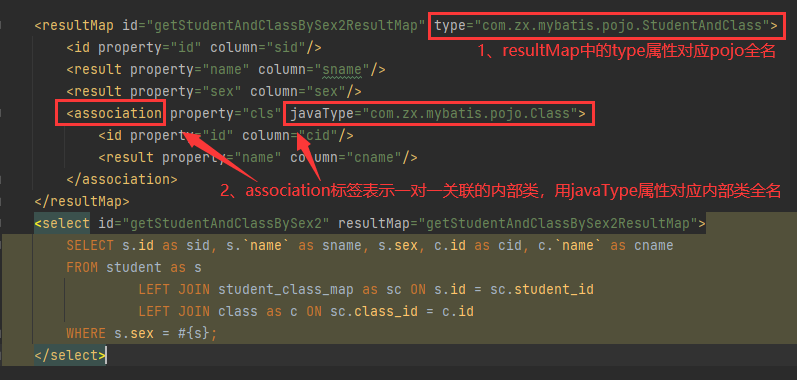
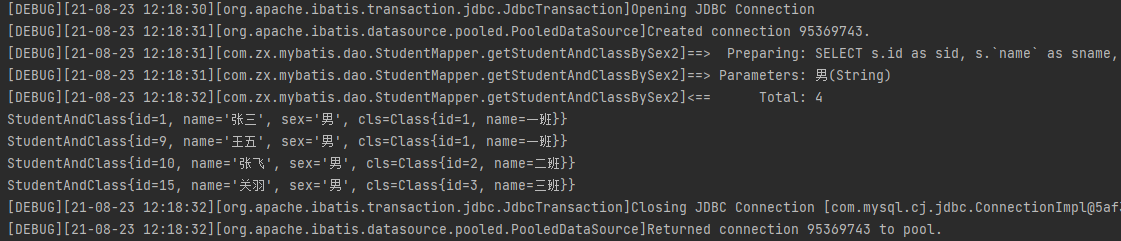
执行查询方法getStudentAndClassBySex2后,结果集映射对象类型为com.zx.mybatis.pojo.StudentAndClass,
过程中字段有通过property属性进行原始字段column的重命名。由于StudentAndClass对象中包含内部类,
需要使用标签association表示关联一对一对象,标签的javaType属性表示内部类的类型。pojo结构如下:
public class StudentAndClass {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Class cls;
}public class Class {
private String id;
private String name;
}
@Test
public void getStudentAndClassBySex2() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
for (StudentAndClass studentAndClass : mapper.getStudentAndClassBySex2("男")) {
System.out.println(studentAndClass);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void getStudentAndClassBySex2() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<StudentAndClass> list = mapper.getStudentAndClassBySex2("男");
for (StudentAndClass studentAndClass : list) {
System.out.println(studentAndClass);
}
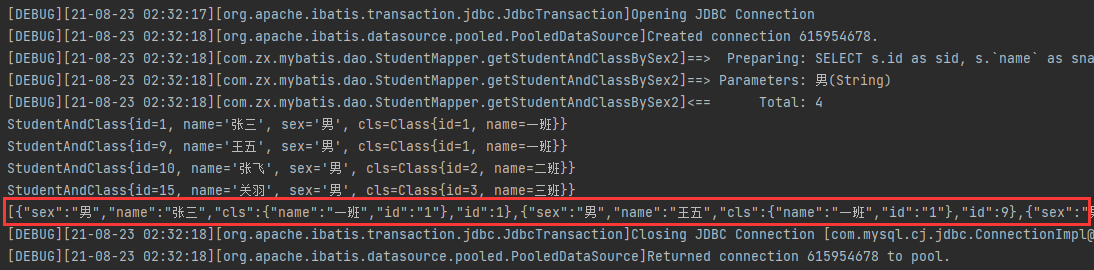
//输出json
System.out.println(JSON.toJSON(list));
sqlSession.close();
} 
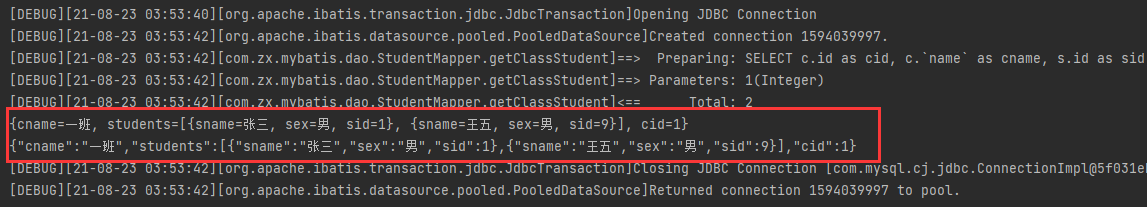
四、一对多型映射
一对多型特征是pojo中包含内部类列表。
- mapper中编写方法:
- 映射文件中写查询:
- 编写测试代码:
- 运行查看结果:
List<StudentAndClass> getStudentAndClassBySex2(String s);
和一对一类似的mapper映射文件写法:
执行查询方法getClassStudent2后,结果集映射对象类型为com.zx.mybatis.pojo.ClassStudent,
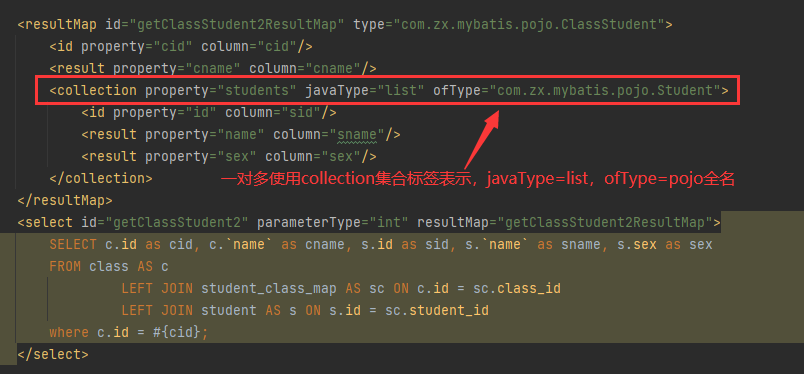
过程中字段有通过property属性进行原始字段column的重命名。由于ClassStudent对象中包含内部类的List对象,
需要使用标签collection表示关联集合,javaType属性表示内部类的List类型,ofType属性表示List所封装的类型。
pojo结构如下:
public class ClassStudent {
private String cid;
private String cname;
private List<Student> students;
}public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
}
@Test
public void getClassStudent2() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
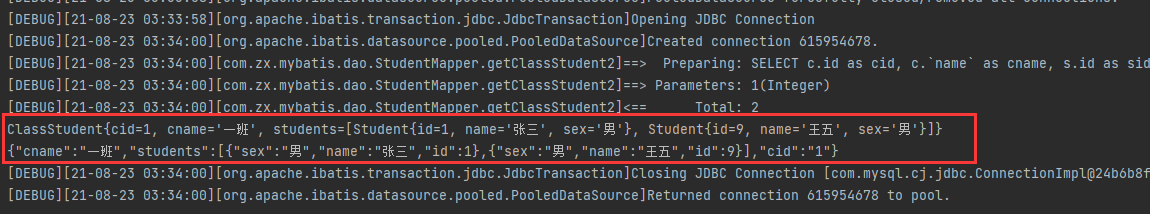
ClassStudent classStudent2 = mapper.getClassStudent2(1);
System.out.println(classStudent2);
Object jsonStr = JSON.toJSON(classStudent2);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
sqlSession.close();
}
五、复杂映射为Map+List
除了将复杂映射为一对一和一对多的pojo对象,还可以将其映射为Map和List,如果实际开发中,不需要构造pojo对象进行复杂逻辑,只是将查询的记过数据返回到客户端,
完全可以使用Map和List对象映射,这样做可以省去构建pojo工作。
- 一对一:
- 一对多:
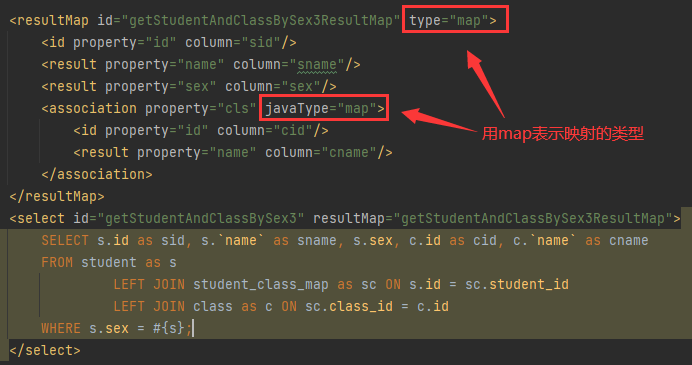
resultMap标签中的type属性和association标签中的javaType属性,都用map,
结合上述一对一映射为简单pojo原理可以联想到,这里也是将查询结果映射为map+内部map结构。
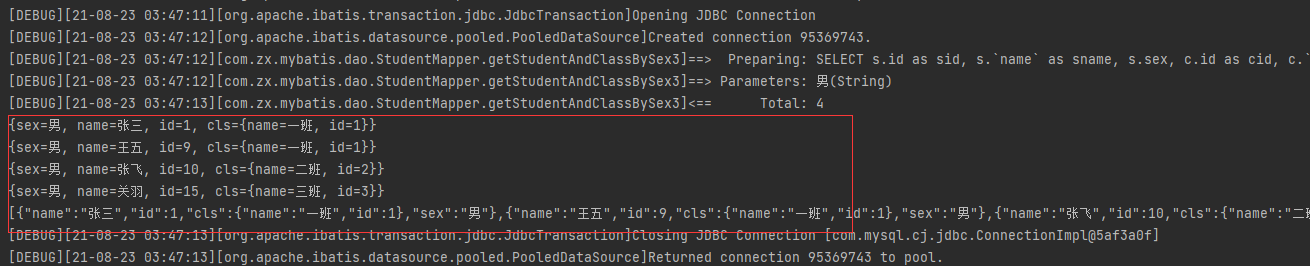
编写测试方法输出结果如下:
@Test
public void getStudentAndClassBySex3() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Map<Object, Object>> list = mapper.getStudentAndClassBySex3("男");
for (Map<Object, Object> map : list) {
System.out.println(map);
}
Object jsonStr = JSON.toJSON(list);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
sqlSession.close();
} 
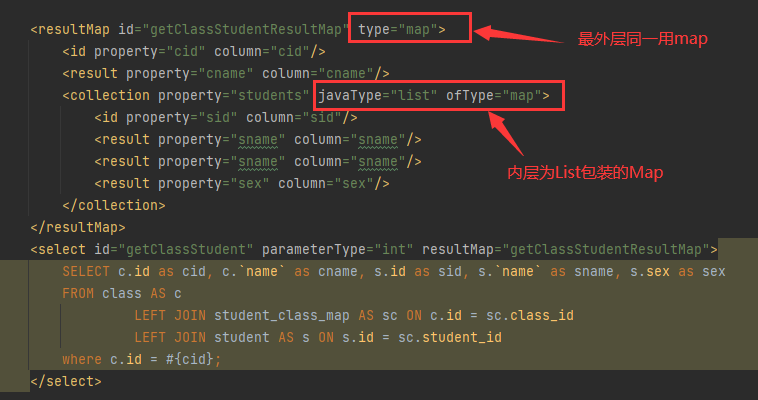
resultMap标签中的type属性用map,association标签中javaType属性用list,
ofType属性用map表示内部为:List所封装的Map结构。
编写测试方法输出结果如下:
@Test
public void getClassStudent() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Map<Object, Object> classStudent = mapper.getClassStudent(1);
System.out.println(classStudent);
Object jsonStr = JSON.toJSON(classStudent);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
sqlSession.close();
}