2. Connector组件-请求处理的主角
有了整体架构的概念就知道,原来是connector组件在处理着一切的请求,
那么它是如何工作的呢。
下面慢慢分析
源码以tomcat-embed-9.0.17为例进行分析
Connector
先看看connector是个什么东东
//org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector
public class Connector extends LifecycleMBeanBase {
}
1.类图
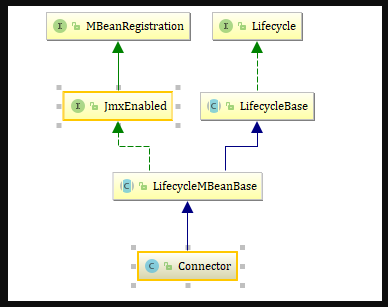
继承了LifecycleMBeanBase,生命周期管理
需要实现以下方法,主要流程相关的方法都在这几个方法里
protected abstract void initInternal() throws LifecycleException;
protected abstract void startInternal() throws LifecycleException;
protected abstract void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException;
protected abstract void destroyInternal() throws LifecycleException;
2.主要属性
protocolHandler 协议处理类
protected final ProtocolHandler protocolHandler;
protected Service service;
//默认NioProtocal
public Connector() {
this("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol");
}
2.1 protocolHandler是个什么鬼
是一个接口
public interface ProtocolHandler {
}
看看他的实现类都有什么呢

像是一个处理各种协议的接口 HTTP、AJP(至于AJP协议是个什么鬼,AJP 全称Apache JServ Protocol, 是定向包协议,因为性能的原因,使用二进制格式来传输可读性文本,WEB服务器通过TCP连接和SERVLET容器连接。)
这应该就是处理请求的核心类,后面会详细讲解。先看看connector组件工作流程吧
3.工作流程
initInternal
初始化了protocolHandler
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
if (this.protocolHandler == null) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"));
} else {
this.adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
this.protocolHandler.setAdapter(this.adapter);
if (this.service != null) {
this.protocolHandler.setUtilityExecutor(this.service.getServer().getUtilityExecutor());
}
if (null == this.parseBodyMethodsSet) {
this.setParseBodyMethods(this.getParseBodyMethods());
}
if (this.protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprLifecycleListener.isInstanceCreated()) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprListener", new Object[]{this.getProtocolHandlerClassName()}));
} else if (this.protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable()) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprLibrary", new Object[]{this.getProtocolHandlerClassName()}));
} else {
if (AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() && AprLifecycleListener.getUseOpenSSL() && this.protocolHandler instanceof AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol) {
AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?> jsseProtocolHandler = (AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol)this.protocolHandler;
if (jsseProtocolHandler.isSSLEnabled() && jsseProtocolHandler.getSslImplementationName() == null) {
jsseProtocolHandler.setSslImplementationName(OpenSSLImplementation.class.getName());
}
}
try {
this.protocolHandler.init();
} catch (Exception var2) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), var2);
}
}
}
}
startInternal
启动了protocolHandler
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if (this.getPortWithOffset() < 0) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.invalidPort", new Object[]{this.getPortWithOffset()}));
} else {
this.setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
try {
this.protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception var2) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), var2);
}
}
}
stopInternal
停止了protocolHandler
protected void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
this.setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING);
try {
if (this.protocolHandler != null) {
this.protocolHandler.stop();
}
} catch (Exception var2) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStopFailed"), var2);
}
}
destroyInternal
销毁了protocolHandler
protected void destroyInternal() throws LifecycleException {
try {
if (this.protocolHandler != null) {
this.protocolHandler.destroy();
}
} catch (Exception var2) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerDestroyFailed"), var2);
}
if (this.getService() != null) {
this.getService().removeConnector(this);
}
super.destroyInternal();
}
下一篇讲解protocolHandler是个什么鬼


