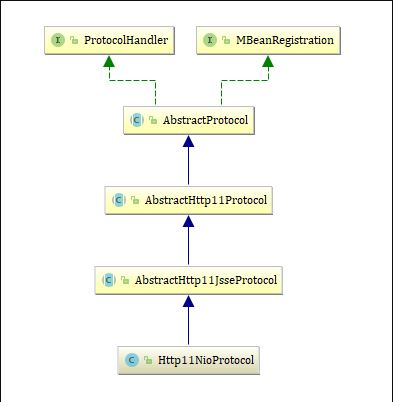
2.1 protocolHandler
上一篇讲了connector组件主要和这个protocolHandler打交道了
那么看看这到底是个什么鬼
就从默认的ProtocolHandler看看吧
1.Http11NioProtocol
源码就下面这么点,这么简短??!!
public class Http11NioProtocol extends AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<NioChannel> {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(Http11NioProtocol.class);
public Http11NioProtocol() {
super(new NioEndpoint());
}
protected Log getLog() {
return log;
}
public void setPollerThreadCount(int count) {
((NioEndpoint)this.getEndpoint()).setPollerThreadCount(count);
}
public int getPollerThreadCount() {
return ((NioEndpoint)this.getEndpoint()).getPollerThreadCount();
}
public void setSelectorTimeout(long timeout) {
((NioEndpoint)this.getEndpoint()).setSelectorTimeout(timeout);
}
public long getSelectorTimeout() {
return ((NioEndpoint)this.getEndpoint()).getSelectorTimeout();
}
public void setPollerThreadPriority(int threadPriority) {
((NioEndpoint)this.getEndpoint()).setPollerThreadPriority(threadPriority);
}
public int getPollerThreadPriority() {
return ((NioEndpoint)this.getEndpoint()).getPollerThreadPriority();
}
protected String getNamePrefix() {
return this.isSSLEnabled() ? "https-" + this.getSslImplementationShortName() + "-nio" : "http-nio";
}
}
就看到了 构造函数初始化了一个叫NioEndpoint的东东,看来这个东西很关键,先不管他
上篇讲到connector就干了几件事,初始化、启动、停止、销毁protocol
那么看看这几个方法里protocol都干了什么
1.1 工作流程
init
一直往上看,会发现init方法的实现都在AbstractHttp11Protocol和AbstractProtocol里
AbstractHttp11Protocol
public void init() throws Exception {
Iterator var1 = this.upgradeProtocols.iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = (UpgradeProtocol)var1.next();
this.configureUpgradeProtocol(upgradeProtocol);
}
super.init();
}
调用了父类AbstractProtocol的init
public void init() throws Exception {
if (this.getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
this.getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.init", new Object[]{this.getName()}));
this.logPortOffset();
}
if (this.oname == null) {
this.oname = this.createObjectName();
if (this.oname != null) {
Registry.getRegistry((Object)null, (Object)null).registerComponent(this, this.oname, (String)null);
}
}
if (this.domain != null) {
this.rgOname = new ObjectName(this.domain + ":type=GlobalRequestProcessor,name=" + this.getName());
Registry.getRegistry((Object)null, (Object)null).registerComponent(this.getHandler().getGlobal(), this.rgOname, (String)null);
}
String endpointName = this.getName();
this.endpoint.setName(endpointName.substring(1, endpointName.length() - 1));
this.endpoint.setDomain(this.domain);
this.endpoint.init();
}
看来看去 还是觉得这句话最关键 this.endpoint.init();
初始化了endpoint
start
看看start里干了什么吧
还是AbstractProtocol里
public void start() throws Exception {
if (this.getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
this.getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start", new Object[]{this.getName()}));
this.logPortOffset();
}
this.endpoint.start();
this.monitorFuture = this.getUtilityExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
if (!AbstractProtocol.this.isPaused()) {
AbstractProtocol.this.startAsyncTimeout();
}
}
}, 0L, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
启动了endpoint
stop
不用说啊,stop里停止了endpoint
public void stop() throws Exception {
if (this.getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
this.getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.stop", new Object[]{this.getName()}));
this.logPortOffset();
}
if (this.monitorFuture != null) {
this.monitorFuture.cancel(true);
this.monitorFuture = null;
}
this.stopAsyncTimeout();
Iterator var1 = this.waitingProcessors.iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
Processor processor = (Processor)var1.next();
processor.timeoutAsync(-1L);
}
this.endpoint.stop();
}
一看果然是
destory
public void destroy() throws Exception {
if (this.getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
this.getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.destroy", new Object[]{this.getName()}));
this.logPortOffset();
}
try {
this.endpoint.destroy();
} finally {
if (this.oname != null) {
if (this.mserver == null) {
Registry.getRegistry((Object)null, (Object)null).unregisterComponent(this.oname);
} else {
try {
this.mserver.unregisterMBean(this.oname);
} catch (InstanceNotFoundException | MBeanRegistrationException var7) {
this.getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocol.mbeanDeregistrationFailed", new Object[]{this.oname, this.mserver}));
}
}
}
if (this.rgOname != null) {
Registry.getRegistry((Object)null, (Object)null).unregisterComponent(this.rgOname);
}
}
}
看来这个protocolHandler和endpoint杠上了,看来这个endpoint是个关键,下一篇详细解析他