2.2 EndPoint
上一篇protocolHandler和endpoint联系密切
那么看看endpoint是个什么东东
不看不知道,一看不得了,这个类的源码就有点多了。
按照惯例看看架构图
看起来还挺简单
整个体系的构图也很简单
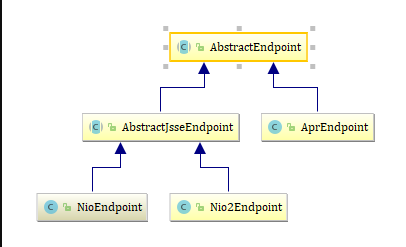
看看有什么重要属性吧
2.NioEndpoint
2.1 重要属性
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(NioEndpoint.class);
public static final int OP_REGISTER = 256;
private NioSelectorPool selectorPool = new NioSelectorPool();
private volatile ServerSocketChannel serverSock = null;
private volatile CountDownLatch stopLatch = null;
private SynchronizedStack<NioEndpoint.PollerEvent> eventCache;
private SynchronizedStack<NioChannel> nioChannels;
private boolean useInheritedChannel = false;
private int pollerThreadPriority = 5;
private int pollerThreadCount = Math.min(2, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
private long selectorTimeout = 1000L;
private NioEndpoint.Poller[] pollers = null;
private AtomicInteger pollerRotater = new AtomicInteger(0);
一堆属性,没有头绪,不着急,慢慢分析,会找到头绪的
根据上一篇protocolHandler工作流程看看每一步endpoint都干了什么吧
endpoint声明在AbstractProtocol里
private final AbstractEndpoint<S, ?> endpoint;
2.2 init
首先调用AbstractEndpoint的init方法
public final void init() throws Exception {
if (this.bindOnInit) {
this.bindWithCleanup();
this.bindState = AbstractEndpoint.BindState.BOUND_ON_INIT;
}
if (this.domain != null) {
this.oname = new ObjectName(this.domain + ":type=ThreadPool,name="" + this.getName() + """);
Registry.getRegistry((Object)null, (Object)null).registerComponent(this, this.oname, (String)null);
ObjectName socketPropertiesOname = new ObjectName(this.domain + ":type=ThreadPool,name="" + this.getName() + "",subType=SocketProperties");
this.socketProperties.setObjectName(socketPropertiesOname);
Registry.getRegistry((Object)null, (Object)null).registerComponent(this.socketProperties, socketPropertiesOname, (String)null);
SSLHostConfig[] var2 = this.findSslHostConfigs();
int var3 = var2.length;
for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {
SSLHostConfig sslHostConfig = var2[var4];
this.registerJmx(sslHostConfig);
}
}
}
private void bindWithCleanup() throws Exception {
try {
this.bind();
} catch (Throwable var2) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(var2);
this.unbind();
throw var2;
}
}
bind方法是个抽象方法,需要子类去实现,看看在哪实现的
bind
就在NioEndpoint这个类里
public void bind() throws Exception {
this.initServerSocket();
if (this.acceptorThreadCount == 0) {
this.acceptorThreadCount = 1;
}
if (this.pollerThreadCount <= 0) {
this.pollerThreadCount = 1;
}
this.setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(this.pollerThreadCount));
this.initialiseSsl();
this.selectorPool.open();
}
protected void initServerSocket() throws Exception {
if (!this.getUseInheritedChannel()) {
this.serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open();
this.socketProperties.setProperties(this.serverSock.socket());
InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(this.getAddress(), this.getPortWithOffset());
this.serverSock.socket().bind(addr, this.getAcceptCount());
} else {
Channel ic = System.inheritedChannel();
if (ic instanceof ServerSocketChannel) {
this.serverSock = (ServerSocketChannel)ic;
}
if (this.serverSock == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("endpoint.init.bind.inherited"));
}
}
this.serverSock.configureBlocking(true);
}
看看干了些什么呢
- initServerSocket
初始化了serverSocket - 设置了一堆属性什么的
- this.selectorPool.open();
开启了selectorPool
基本和Nio有关,没有Nio知识根本不知道这是些啥
NIO会在【网络请求-Java篇详解】
现在暂时不管他,继续往下看
2.3 start
start干了些啥呢
依旧从AbstractEndpoint开始
public final void start() throws Exception {
if (this.bindState == AbstractEndpoint.BindState.UNBOUND) {
this.bindWithCleanup();
this.bindState = AbstractEndpoint.BindState.BOUND_ON_START;
}
this.startInternal();
}
startInternal又是个抽象方法
startInternal
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!this.running) {
this.running = true;
this.paused = false;
this.processorCache = new SynchronizedStack(128, this.socketProperties.getProcessorCache());
this.eventCache = new SynchronizedStack(128, this.socketProperties.getEventCache());
this.nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack(128, this.socketProperties.getBufferPool());
if (this.getExecutor() == null) {
this.createExecutor();
}
this.initializeConnectionLatch();
this.pollers = new NioEndpoint.Poller[this.getPollerThreadCount()];
for(int i = 0; i < this.pollers.length; ++i) {
this.pollers[i] = new NioEndpoint.Poller();
Thread pollerThread = new Thread(this.pollers[i], this.getName() + "-ClientPoller-" + i);
pollerThread.setPriority(this.threadPriority);
pollerThread.setDaemon(true);
pollerThread.start();
}
this.startAcceptorThreads();
}
}
//AbstractEndpoint里
public void createExecutor() {
this.internalExecutor = true;
TaskQueue taskqueue = new TaskQueue();
TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(this.getName() + "-exec-", this.daemon, this.getThreadPriority());
this.executor = new org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor(this.getMinSpareThreads(), this.getMaxThreads(), 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, taskqueue, tf);
taskqueue.setParent((org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor)this.executor);
}
protected LimitLatch initializeConnectionLatch() {
if (this.maxConnections == -1) {
return null;
} else {
if (this.connectionLimitLatch == null) {
this.connectionLimitLatch = new LimitLatch((long)this.getMaxConnections());
}
return this.connectionLimitLatch;
}
}
protected void startAcceptorThreads() {
int count = this.getAcceptorThreadCount();
this.acceptors = new ArrayList(count);
for(int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
Acceptor<U> acceptor = new Acceptor(this);
String threadName = this.getName() + "-Acceptor-" + i;
acceptor.setThreadName(threadName);
this.acceptors.add(acceptor);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptor, threadName);
t.setPriority(this.getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(this.getDaemon());
t.start();
}
}
//这个方法在AbstractEndpoint里
protected void startAcceptorThreads() {
int count = this.getAcceptorThreadCount();
this.acceptors = new ArrayList(count);
for(int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
Acceptor<U> acceptor = new Acceptor(this);
String threadName = this.getName() + "-Acceptor-" + i;
acceptor.setThreadName(threadName);
this.acceptors.add(acceptor);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptor, threadName);
t.setPriority(this.getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(this.getDaemon());
t.start();
}
}
再看看干了些啥
-
依旧设置了一堆属性
-
createExecutor
创建了一个线程池 还是tomcat继承了ThreadPoolExecutor,自己封装了一下 -
initializeConnectionLatch
初始化了连接锁 看名字是用来限制连接数的 -
pollerThread.start
启动了一个pollerThread -
startAcceptorThreads
启动了一个acceptor的线程
2.4 初始化+启动 总结
startInternal 方法都看完了,理论上tomcat都启动了,
可是看到这也没看出啥,到底怎么接受请求的啊
仔细查看上面的每一步
看看到底有什么猫腻
看着看着才知道
真正的精彩之处才刚刚开始呢
请看下篇【EndPoint组件】
2.5 stop
依旧从AbstractEndpoint开始
public final void stop() throws Exception {
this.stopInternal();
if (this.bindState == AbstractEndpoint.BindState.BOUND_ON_START || this.bindState == AbstractEndpoint.BindState.SOCKET_CLOSED_ON_STOP) {
this.unbind();
this.bindState = AbstractEndpoint.BindState.UNBOUND;
}
}
stopInternal
public void stopInternal() {
if (!this.paused) {
this.pause();
}
if (this.running) {
this.running = false;
for(int i = 0; this.pollers != null && i < this.pollers.length; ++i) {
if (this.pollers[i] != null) {
this.pollers[i].destroy();
this.pollers[i] = null;
}
}
try {
if (!this.getStopLatch().await(this.selectorTimeout + 100L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
log.warn(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.stopLatchAwaitFail"));
}
} catch (InterruptedException var2) {
log.warn(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.stopLatchAwaitInterrupted"), var2);
}
this.shutdownExecutor();
this.eventCache.clear();
this.nioChannels.clear();
this.processorCache.clear();
}
}
unbind
public void unbind() throws Exception {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Destroy initiated for " + new InetSocketAddress(this.getAddress(), this.getPortWithOffset()));
}
if (this.running) {
this.stop();
}
this.doCloseServerSocket();
this.destroySsl();
super.unbind();
if (this.getHandler() != null) {
this.getHandler().recycle();
}
this.selectorPool.close();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Destroy completed for " + new InetSocketAddress(this.getAddress(), this.getPortWithOffset()));
}
}


