Python中精选的logging模块,你吃惊了没?

用Python写代码的时候,在想看的地方写个print(xx) 就能在控制台上显示打印信息,这样子就能知道它是什么了,但是当我需要看大量的地方或者在一个文件中查看的时候,这时候print就不大方便了,所以Python引入了logging模块来记录想要的信息。
1 日志级别
import logging # 引入logging模块 # 将信息打印到控制台上 logging.debug(u"debug") logging.info(u"info") logging.warning(u"warning") logging.error(u"error") logging.critical(u"critical")
回显:

上面可以看到只有后面三个能打印出来
默认生成的root logger的level是logging.WARNING,低于该级别的就不输出了
级别排序:CRITICAL > ERROR > WARNING > INFO > DEBUG
debug : 打印全部的日志,详细的信息,通常只出现在诊断问题上
info : 打印info,warning,error,critical级别的日志,确认一切按预期运行
warning : 打印warning,error,critical级别的日志,一个迹象表明,一些意想不到的事情发生了,或表明一些问题在不久的将来(例如。磁盘空间低”),这个软件还能按预期工作
error : 打印error,critical级别的日志,更严重的问题,软件没能执行一些功能
critical : 打印critical级别,一个严重的错误,这表明程序本身可能无法继续运行
这时候,如果需要显示低于WARNING级别的内容,可以引入NOTSET级别来显示:
import logging # 引入logging模块 logging.basicConfig(level=logging.NOTSET) # 设置日志级别 logging.debug(u"如果设置了日志级别为NOTSET,那么这里可以采取debug、info的级别的内容也可以显示在控制台上了")
回显:
 2 部分名词解释
2 部分名词解释
print也可以输入日志,logging相对print来说更好控制输出在哪个地方,怎么输出及控制消息级别来过滤掉那些不需要的信息。
Logging.Formatter:这个类配置了日志的格式,在里面自定义设置日期和时间,输出日志的时候将会按照设置的格式显示内容。
Logging.Logger:Logger是Logging模块的主体,进行以下三项工作:
1、为程序提供记录日志的接口
2、判断日志所处级别,并判断是否要过滤
3、根据其日志级别将该条日志分发给不同handler
常用函数有:
Logger.setLevel() 设置日志级别
Logger.addHandler() 和 Logger.removeHandler() 添加和删除一个Handler
Logger.addFilter() 添加一个Filter,过滤作用
Logging.Handler:Handler基于日志级别对日志进行分发,如设置为WARNING级别的Handler只会处理WARNING及以上级别的日志。
3 日志输出-控制台
import logging # 引入logging模块
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,
format='%(asctime)s - %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] - %(levelname)s: %(message)s') # logging.basicConfig函数对日志的输出格式及方式做相关配置
# 由于日志基本配置中级别设置为DEBUG,所以一下打印信息将会全部显示在控制台上
logging.info('this is a loggging info message')
logging.debug('this is a loggging debug message')
logging.warning('this is loggging a warning message')
logging.error('this is an loggging error message')
logging.critical('this is a loggging critical message')
上面代码通过logging.basicConfig函数进行配置了日志级别和日志内容输出格式;因为级别为DEBUG,所以会将DEBUG级别以上的信息都输出显示再控制台上。
回显:
 4 日志输出-文件
4 日志输出-文件
import logging # 引入logging模块
import os
import time
# 第一步,创建一个logger
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO) # Log等级总开关
# 第二步,创建一个handler,用于写入日志文件
rq = time.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M', time.localtime(time.time()))
log_path = os.path.dirname(os.getcwd()) + '/Logs/'
# 如果日志目录不存在,就创建
if not os.path.exists(log_path):
os.mkdir(log_path)
log_name = log_path + rq + '.log'
logfile = log_name
fh = logging.FileHandler(logfile, mode='w')
fh.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) # 输出到file的log等级的开关
# 第三步,定义handler的输出格式
formatter = logging.Formatter("%(asctime)s - %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] - %(levelname)s: %(message)s")
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
# 第四步,将logger添加到handler里面
logger.addHandler(fh)
# 日志
logger.debug('this is a logger debug message')
logger.info('this is a logger info message')
logger.warning('this is a logger warning message')
logger.error('this is a logger error message')
logger.critical('this is a logger critical message')
回显(打开同一目录下生成的文件):

文件内容:
 5 日志输出-控制台和文件
5 日志输出-控制台和文件
只要在输入到日志中的第三步和第四步插入一个handler输出到控制台:
# 创建一个handler,用于输出到控制台 ch = logging.StreamHandler() ch.setLevel(logging.WARNING) # 输出到console的log等级的开关 # 第三步和第四步分别加入以下代码即可 ch.setFormatter(formatter) logger.addHandler(ch)
6 format常用格式说明
%(levelno)s: 打印日志级别的数值
%(levelname)s: 打印日志级别名称
%(pathname)s: 打印当前执行程序的路径,其实就是sys.argv[0]
%(filename)s: 打印当前执行程序名
%(funcName)s: 打印日志的当前函数
%(lineno)d: 打印日志的当前行号
%(asctime)s: 打印日志的时间
%(thread)d: 打印线程ID
%(threadName)s: 打印线程名称
%(process)d: 打印进程ID
%(message)s: 打印日志信息
7 捕捉异常,用traceback记录
import os.path
import time
import logging
# 创建一个logger
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO) # Log等级总开关
# 创建一个handler,用于写入日志文件
rq = time.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M', time.localtime(time.time()))
log_path = os.path.dirname(os.getcwd()) + '/Logs/'
# 如果日志目录不存在,就创建
if not os.path.exists(log_path):
os.mkdir(log_path)
log_name = log_path + rq + '.log'
logfile = log_name
fh = logging.FileHandler(logfile, mode='w')
fh.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) # 输出到file的log等级的开关
# 定义handler的输出格式
formatter = logging.Formatter("%(asctime)s - %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] - %(levelname)s: %(message)s")
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(fh)
# 使用logger.XX来记录错误,这里的"error"可以根据所需要的级别进行修改
try:
open('/path/to/does/not/exist', 'rb')
except (SystemExit, KeyboardInterrupt):
raise
except Exception as e:
logger.error('Failed to open file', exc_info=True)
回显(存储在文件中):
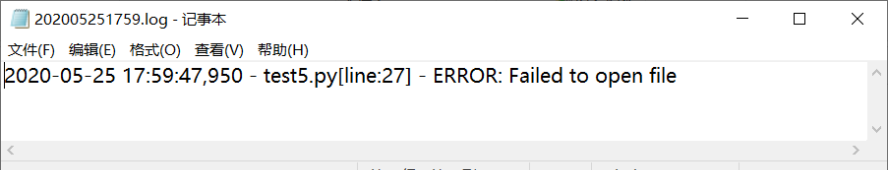
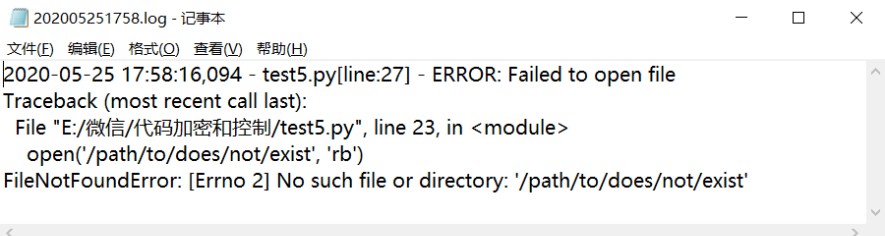 如果需要将日志不上报错误,仅记录,可以将exc_info=False,回显如下:
如果需要将日志不上报错误,仅记录,可以将exc_info=False,回显如下:
 8 多模块调用logging,日志输出顺序
8 多模块调用logging,日志输出顺序
warning_output.py
import logging def write_warning(): logging.warning(u"记录文件warning_output.py的日志")
error_output.py
import logging def write_error(): logging.error(u"记录文件error_output.py的日志")
main.py
import logging import warning_output import error_output def write_critical(): logging.critical(u"记录文件main.py的日志") warning_output.write_warning() # 调用warning_output文件中write_warning方法 write_critical() error_output.write_error() # 调用error_output文件中write_error方法
回显:

从上面来看,日志的输出顺序和模块执行顺序是一致的。
9 日志滚动和过期删除
# coding:utf-8
import logging
import time
import re
from logging.handlers import TimedRotatingFileHandler
from logging.handlers import RotatingFileHandler
def backroll():
# 日志打印格式
log_fmt = '%(asctime)s File "%(filename)s",line %(lineno)s %(levelname)s: %(message)s'
formatter = logging.Formatter(log_fmt)
# 创建TimedRotatingFileHandler对象
log_file_handler = TimedRotatingFileHandler(filename="ds_update", when="M", interval=2, backupCount=2)
# log_file_handler.suffix = "%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M.log"
# log_file_handler.extMatch = re.compile(r"^d{4}-d{2}-d{2}_d{2}-d{2}.log$")
log_file_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
log = logging.getLogger()
log.addHandler(log_file_handler)
# 循环打印日志
log_content = "test log"
count = 0
while count < 30:
log.error(log_content)
time.sleep(20)
count = count + 1
log.removeHandler(log_file_handler)
if __name__ == "__main__":
backroll()
filename:日志文件名的prefix;
when:是一个字符串,用于描述滚动周期的基本单位,字符串的值及意义如下:
“S”: Seconds
“M”: Minutes
“H”: Hours
“D”: Days
“W”: Week day (0=Monday)
“midnight”: Roll over at midnight
interval: 滚动周期,单位有when指定,比如:when=’D’,interval=1,表示每天产生一个日志文件
backupCount: 表示日志文件的保留个数
更多Python知识,请关注云海天Python教程!!
来源:PY学习网:原文地址:https://www.py.cn/article.html

