Python之IO多路复用是什么

IO multiplexing(IO多路复用)
IO多路复用,有些地方称之为event driven IO(事件驱动IO)。
它的好处在于单个进程可以处理多个网络IO请求。select/epoll这两个是函数,它会不断轮询所有的socket,直到某个socket就绪有数据可达,就会通知用户进程,当用户进程调用了select函数,select是一个阻塞方法,会把进程阻塞住,同时会监听所有select负责的socket,当任何一个socket中的数据准备好了,select就会返回。这个时候用户进程再调用readRecv操作,将数据从内核拷贝到用户进程。
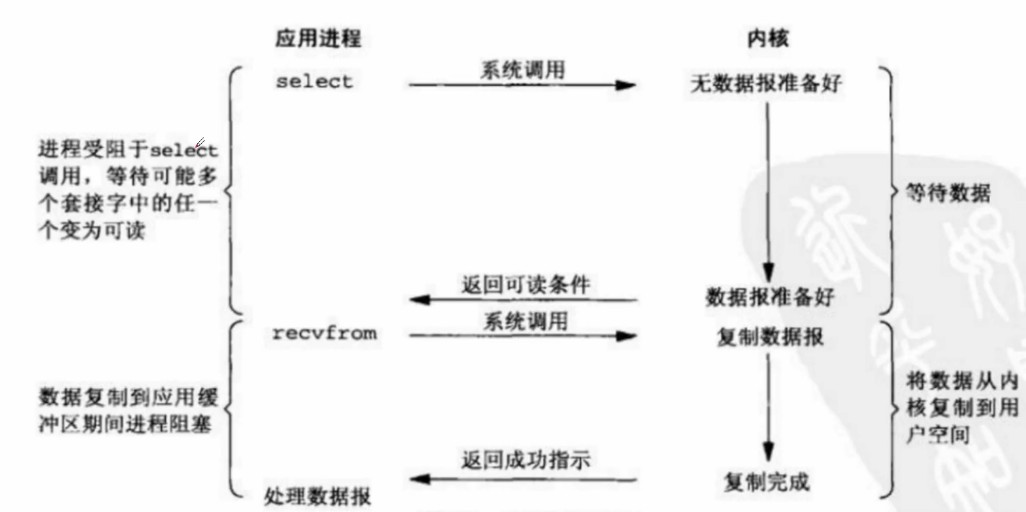
select虽然是阻塞的,但是它的优势在于它可以用一个进程处理多个连接,这个利用非阻塞的轮询方式是无法实现的,当连接数增多时优势就明显,而对于单个连接则跟同步IO区别不大甚至性能还要更低。
select,poll,epoll都是IO多路复用的机制,IO多路复用就是通过机制用一个进程监视多个描述符,一旦某个描述符就绪(可读或者可写或者异常),能够通知进程进行响应的操作。但是select,poll,epoll本质上是同步IO,因为他们都需要在读写事件就绪后自己负责读写,这个过程是阻塞的。
相关推荐:《Python相关教程》
下面用Python的socket编程模拟IO多路复用(IO多路复用+回调+事件循环)
class Fetcher:
def connected(self, key):
selector.unregister(key.fd)
self.con.send('GET {} HTTP/1.1
Host:{}
Connection:close
'.format(self.path,self.host).
encode('utf-8'))
selector.register(self.con.fileno(), EVENT_READ, self.read)
def read(self, key):
d = self.con.recv(1024)
if d:
print(d)
self.data += d
else:
selector.unregister(key.fd)
self.data = self.data.decode('utf-8')
html_data = self.data.split('
')[1]
print(html_data)
self.con.close()
def get_url(self, url):
...
self.con = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.con.setblocking(False)
#设置非阻塞
try:
self.con.connect((self.host, 80))
except BlockingIOError as e:
pass
selector.register(self.con.fileno(), EVENT_WRITE, self.connected)
过程:发送一个socket请求设置为非阻塞,在select函数中注册事件,self.con.fileno表示当前连接在进程中的描述符,EVENT_WRITE表示socket准备是否就绪,self.connected为回调函数,准备完成后就调用。selector.unregister(key.fd)取消注册,发送HTTP请求,再调用selector.register(self.con.fileno(), EVENT_READ, self.read)注册,若当前请求内容可读,则调用read回调函数读取出响应内容。
注明:在windows下会调用select函数,而在linux/unix下则会调用epoll函数。
完整代码如下:
import socket
from urllib.parse import urlparse
from selectors import DefaultSelector, EVENT_READ, EVENT_WRITE
selector = DefaultSelector()
class Fetcher:
def connected(self, key):
selector.unregister(key.fd)
self.con.send('GET {} HTTP/1.1
Host:{}
Connection:close
'.format(self.path,self.host).
encode('utf-8'))
selector.register(self.con.fileno(), EVENT_READ, self.read)
def read(self, key):
d = self.con.recv(1024)
if d:
print(d)
self.data += d
else:
selector.unregister(key.fd)
self.data = self.data.decode('utf-8')
html_data = self.data.split('
')[1]
print(html_data)
self.con.close()
def get_url(self, url):
url = urlparse(url)
self.host = url.netloc
self.path = url.path
self.data = b''
if self.path == "":
self.path = '/'
self.con = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.con.setblocking(False)
try:
self.con.connect((self.host, 80))
except BlockingIOError as e:
pass
#注册
selector.register(self.con.fileno(), EVENT_WRITE, self.connected)
def loop():
while True:
ready = selector.select()
for key, mask in ready:
callback = key.data
callback(key)
if __name__ == '__main__':
fetcher = Fetcher()
fetcher.get_url('http://www.baidu.com')
loop()
来源:PY学习网:原文地址:https://www.py.cn/article.html

