使用PostgreSQL保存二进制的Protobuf
前言
PostgreSQL 可以直接存储二进制字段,而上周我学习了通过Protobuf来做grpc通信格式,当然也是可以序列化为二进制存入数据库的,需要的时候从数据库查询出来,通过protobuf来转成对应的Java对象,本文就是来尝试一下这个思路。
PostgreSQL 安装
使用docker来安装PostgreSQL, 参照网站https://hub.docker.com/_/postgres
命令如下
docker run –name my-postgres -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=kentest123$# -d postgres
以上命令会去下载postgresql的image,并运行起来, 如果需要我们程序访问,-p一定要加上,把端口打开,不然程序不能连过去。
docker启动后,可以使用如下命令,同时sh来查看数据库资源
docker exec -it my-postgres sh
再执行psql可以输入select语句
psql -U postgres
l 是显示所有数据库
c 数据库名; 切换到某个数据库,我们使用用户postgres,默认会进入名为postgre的数据库
d 是查看数据库中所有表
d 表名是查看表的定义。
查看表的大小
select pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size(“customer”)) as size;
代码编写
这里直接用JPA来完成数据对数据库的访问
定义一个实体
@Entity
@Table(name = "market_price_byte")
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class MarketPriceByte implements Serializable {
@Id
private String id;
@Column(name = "values", nullable = false)
private byte[] values;
}
MarketPriceByte 对应数据库market_price_byte, 两个字段一个是id, 一个是byte数组,后面用来存我们的protobuf。
定义protobuf文件
定义一个proto文件pricevalue.proto
syntax = "proto3";
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_package = "ken.postgresql.proto";
option java_outer_classname = "PriceValueProto";
option objc_class_prefix = "HLW";
package proto;
message PriceValue {
sint32 date = 1;
double open = 2;
double high = 3;
double low = 4;
double close = 5;
}
message PriceValues {
repeated PriceValue price_value = 1;
}
PriceValue表示一天的股票价格, PriceValues是历史价格,我们就是把它序列化后存入到ProgresSQL里面。
使用上篇用到的maven插件生成对应的Java类
编写代码
首先我们定义一个JpaRepository用来存取数据库记录
public interface MarketPriceByteRepository extends JpaRepository<MarketPriceByte, String> {
}
在配置文件中设置数据库配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgres
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=kentest123$#
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto 设置成 update,是代码有更新的时候,同步更新数据库表
编写一个Service用来存数据到数据库和从数据库取数据
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MarketPriceService {
@Autowired
private MarketPriceByteRepository repository;
public void createMarketPrice() {
MarketPriceByte newMarketPrice = new MarketPriceByte();
newMarketPrice.setId("0000000001");
PriceValue priceValue = PriceValue.newBuilder()
.setDate(100)
.setOpen(1.01)
.setHigh(1.12)
.setLow(1.00)
.setClose(1.11).build();
PriceValue priceValue2 = PriceValue.newBuilder()
.setDate(101)
.setOpen(2.01)
.setHigh(2.12)
.setLow(2.00)
.setClose(2.11).build();
PriceValues priceValues = PriceValues.newBuilder()
.addPriceValue(priceValue)
.addPriceValue(priceValue2)
.build();
newMarketPrice.setValues(priceValues.toByteArray());
log.info("Saving new MarketPrice...");
this.repository.save(newMarketPrice);
}
public void queryAllMarketPrices() {
List<MarketPriceByte> allMarketPrices = this.repository.findAll();
log.info("Number of MarketPrices: " + allMarketPrices.size());
if(allMarketPrices.size() > 0)
{
MarketPriceByte marketPriceByte = allMarketPrices.get(0);
log.info(marketPriceByte.getId());
byte[] values = marketPriceByte.getValues();
try {
PriceValues priceValues = PriceValues.parseFrom(values);
PriceValue priceValue1 = priceValues.getPriceValue(0);
PriceValue priceValue2 = priceValues.getPriceValue(1);
log.info(priceValue1.toString());
log.info(priceValue2.toString());
} catch (InvalidProtocolBufferException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
createMarketPrice 我们hardcode了一个MarketPriceByte对象,Java对象序列化为protobuf
priceValues.toByteArray()
然后通过MarketPriceByteRepository存入数据库
queryAllMarketPrices 将我们存入的数据查询出来,完成从byte[] 转成 Java对象 “PriceValues.parseFrom(values)”
调用代码:
marketPriceService.createMarketPrice();
marketPriceService.queryAllMarketPrices();
调用后,我们到数据库查询,可以看到我们hardcode的那条记录
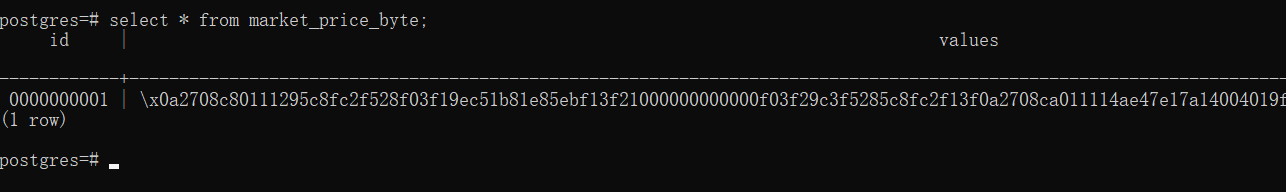
这样就完成了把protobuf对象存入到progresql数据库。
总结
上面的代码比较简单,但对于第一次接触的同学还是有些工作在这里面, 比如docker里面运行postgresql, JPA是否支持postgresql定义的二进制字段, Protobuf生成的对象怎么转成byte[]
这些东西虽然简单,但是也只有自己动手写一写,才印象比较深刻,才更好的理解。
