C++知识点捕捉
C++知识点捕捉
1.对于提高cin运行时间代码:
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);//cin.tie(nullptr);
-
减少运行时间,scanf永远的神
-
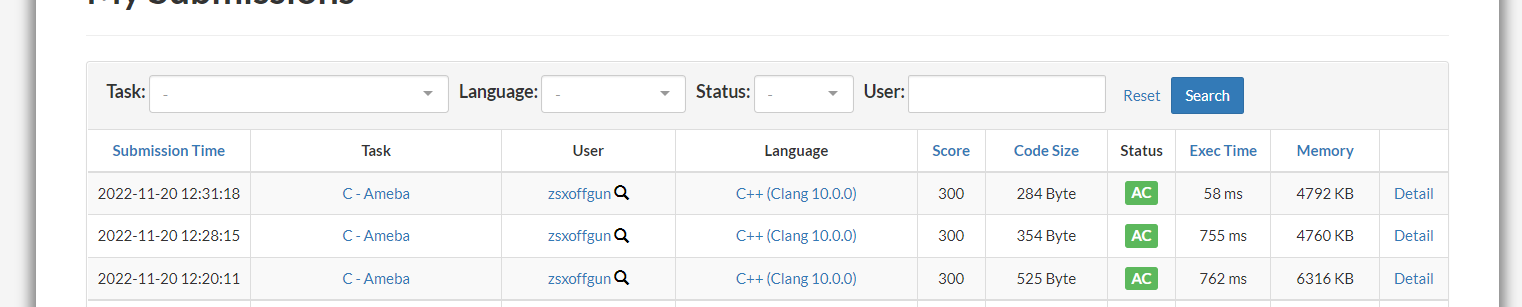
-
13倍,……………………………………
2、提高读入时间的代码:
inline int max(int x,int y){return x>y?x:y;}
inline int min(int x,int y){return x<y?x:y;}
inline int abs(int x){return x>0?x:-x;}
inline void swap(int &x,int &y){int t=x;x=y;y=t;}
inline int read()
{
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while (ch<"0"||ch>"9"){if (ch=="-") f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while (ch>="0"&&ch<="9"){x=x*10+ch-48;ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
3、字符串输入带空格的,只能使用数据类型是char型的。
const int N=100005;
char a[N];
cin.getline(a,N);
- scanf读入string字符串
- 提示,一定不要scanf和cin同时用,一次选用一种,必须。
4结构体的运用语句
struct Edge
{
int a,b,w;
bool operator<(const Edge& W) const
{
return w<W.w;//升序
}
}edges[M];
降序:W.w<w;注意不可改变<
赋值:edges[i]={a,b,w};
5 万能头文件
- 能不用就不用,也会耗费时间,最好记住所用函数具体的库
- 由于C语言没有命名空间,头文件并不存放在命名空间中,因此在C++程序文件中如果用到带后缀.h的头文件时,不必用命名空间。只需在文件中包含所用的头文件即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
6 sort与cmp
struct sno
{
int x,y,z,w,d;
}q[305];
bool cmp(sno a,sno b)
{
if(a.w>b.w) return 1;
else if(a.w<b.w) return 0;
else
{
if(a.x>b.x) return 1;
else if(a.x<b.x) return 0;
else
{
if(a.d>b.d) return 0;
else return 1;
}
}
}
//主函数:sort(q,q+n,cmp);
7.int范围
- -2147483648 ~ 2147483647
- 2^32=4294967296
- 2^31=2,147,483,648
8.二分查找
- 只针对有序序列。
9. c++自带函数耗时长
- 能不用就不用,要不然就自己写一个。比如memset
10.vector 创建二维数组 && 三维数组
- 二维数组
统一赋值
vector<vector<int> > d(n+1,vector<int> (n+1,INF));
INF设置初始值,注意不要超过int类型,否则会溢出,溢出就可能负一个负值。
>>注意一定要有空格> >,要不然会成cout>>,旧的编译器会报错,牛客就会报错
单独赋值
std::vector g2(m,std::array<int,3>{1,2,3});
- 创建非矩形的二维数组
比如
1
1 2
1 2 3
这种类型的二维数组
//未对vector进行初始化赋值,默认为0
vector < vector<int> >f(m);
//创建一个二维数组,m行,然后使用resize对每行的长度进行重置
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
f[i].resize(n);
}
- 三维数组
单独赋值
std::vector dp(m+1, std::array<std::array<int,3>,3>{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9});
统一赋值
int m=20,n=20,p=20;
std::vector< std::vector < std::vector<int> > > g1(m,std::vector< std::vector<int> >(n,std::vector<int>(p,1)));
- 同样可以创建非矩形的三维数组
std::vector<std::vector <std::vector<int> > > g3(m);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
g3[i].resize(n);
}
for(int i=0;i < m;i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++)
{
g3[i][j].resize(p);
}
}
- 实例代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define INF 1e9
int main()
{
int m = 19;
std::vector dp(m+1, std::array<std::array<int,3>,3>{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9});
std::cout << dp[11][0][0] <<" ";
std::cout << dp[18][0][1] <<" ";
std::cout << dp[19][0][2] <<" ";
std::cout << dp[10][1][0] <<" ";
std::cout << dp[13][1][1] <<" ";
std::cout << dp[15][1][2] <<" ";
std::cout << dp[12][2][0] <<" ";
std::cout << dp[17][2][1] <<" ";
std::cout << dp[14][2][2] <<"
";
int n = 20;
std::vector g2(m,std::array<int,3>{1,2,3});
std::cout << g2[2][0]<<" ";
std::cout << g2[2][1]<<" ";
std::cout << g2[2][2]<<"
";
std::vector < std::vector<int> > g(m,std::vector<int>(n,INF));
std::cout << g[10][0] <<" ";
std::cout << g[11][1] <<" ";
std::cout << g[12][2] <<"
";
//未对vector进行初始化赋值,默认为0
std::vector < std::vector<int> > f(m);
//创建一个二维数组,m行,然后使用resize对每行的长度进行重置
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
f[i].resize(n);
}
std::cout << f[1][0] <<" ";
std::cout << f[2][1] <<" ";
std::cout << f[3][8] <<"
";
int p=20;
std::vector< std::vector < std::vector<int> > > g1(m,std::vector< std::vector<int> >(n,std::vector<int>(p,1)));
std::cout << g1[11][0][0] <<" ";
std::cout << g1[18][0][1] <<" ";
std::cout << g1[16][0][2] <<"
";
std::vector<std::vector <std::vector<int> > > g3(m);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
g3[i].resize(n);
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
g3[i][j].resize(p);
}
}
std::cout << g3[11][0][0] <<" ";
std::cout << g3[18][0][1] <<" ";
std::cout << g3[16][0][2] <<"
";
return 0;
}
- 运行结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
1 2 3
1000000000 1000000000 1000000000
0 0 0
1 1 1
0 0 0
11.强制类型转化
1ll*m*n,1ll相当于 long long 类型下的1,
所以1ll*m*n=long long 类型下的m*n
12.建立long long长度的数组技巧
map<ll,ll>a
13.一种主函数内部定义函数方式—方便使用vector及时创建数组时使用
- 必须引进头文件
#include<functional>
function<void(int, int, bool)> search = [&](int L, int R, bool odd)
{
while (L <= R)
{
int mid = L + R >> 1;
int len = 2 * mid - (odd ? 1 : 0);
bool answer = 0;
for (int l = 1, r = l + len - 1; r <= n; ++l, ++r)
{
ULL Lres = LHash[r] - LHash[l - 1] * P[len];
ULL Rres = RHash[l] - RHash[r + 1] * P[len];
if (Lres == Rres)
{
answer = 1;
int i = l + (len + 1) / 2 - 1;
ans = max(ans, len / 2 + same[i]);
}
}
if (answer)
{
L = mid + 1;
}
else R = mid - 1;
}
};//注意分号
14.字符串读入的注意点—有关于从下标1开始读取
char a[N][N];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i]+1;//相当于坐标从1开始,但是原来的0下标位存储的是"/0",所以如果读a[i],那么一定会截止,读到"/0"就结束,注意这里是第二维从1开始,但是我们读a[i]的话,是从第二维的0下标位去读取,所以什么也读不出来
}
15.数组初始化

16.时间复杂度



