day35-IO流02
JavaOI流02
4.常用的类
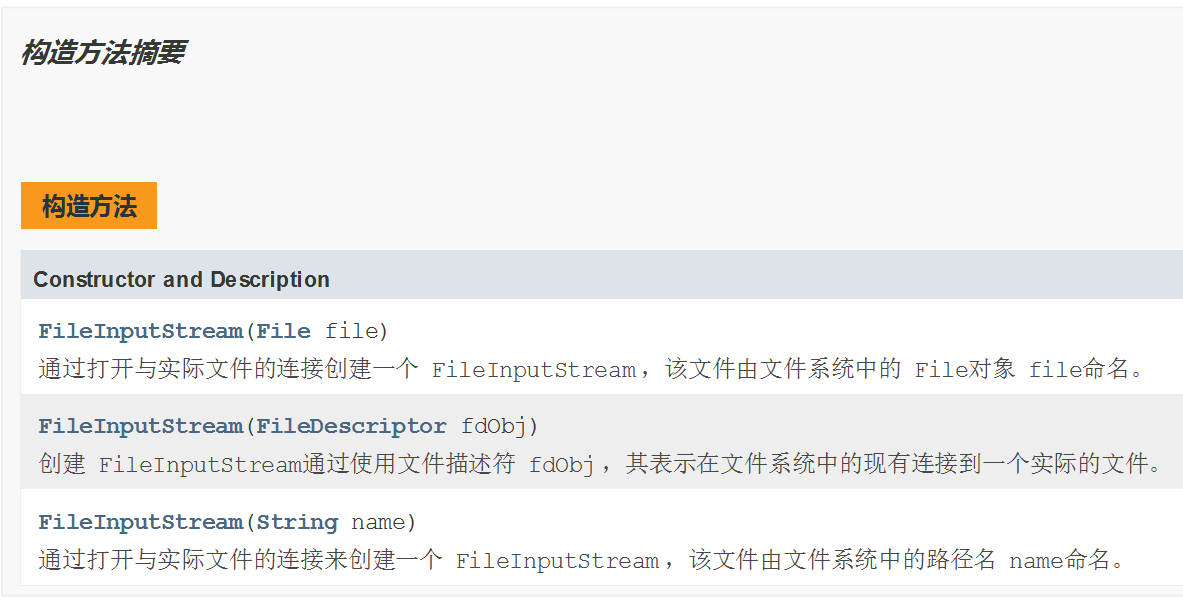
4.1文件字节流输入流-FileInputStream
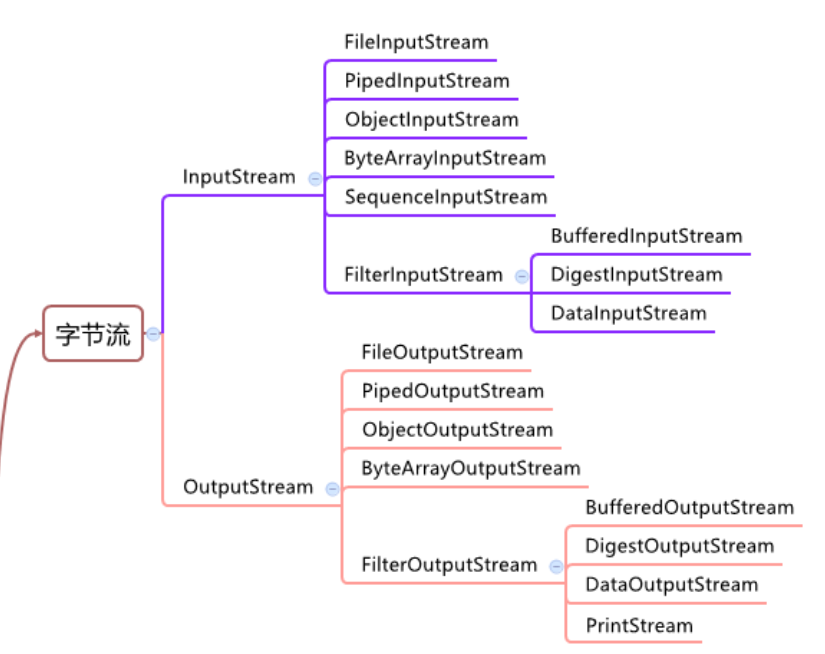
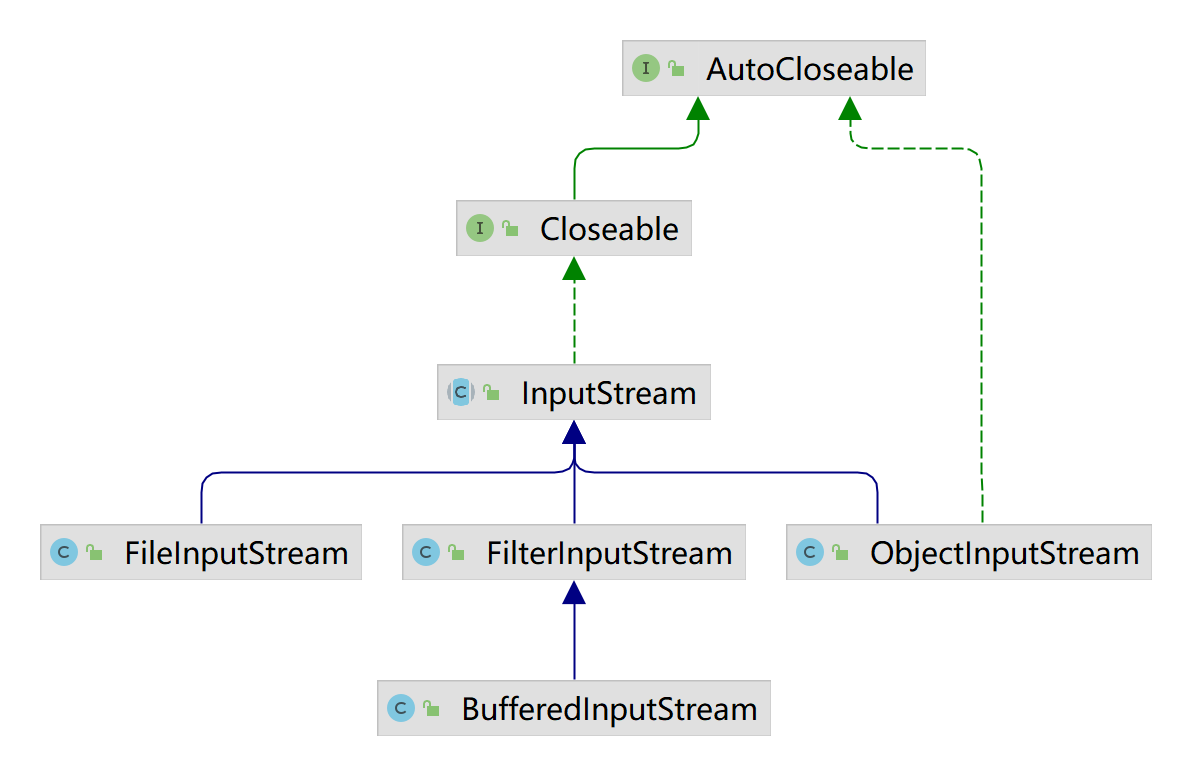
InputStream抽象类是所有类字节输入流的超类
InputStream常用的子类:
- FileInputStream:文件字节输入流
- BufferedInputStream:缓冲字节输入流
- ObjectInputStream:对象字节输入流
常用方法:
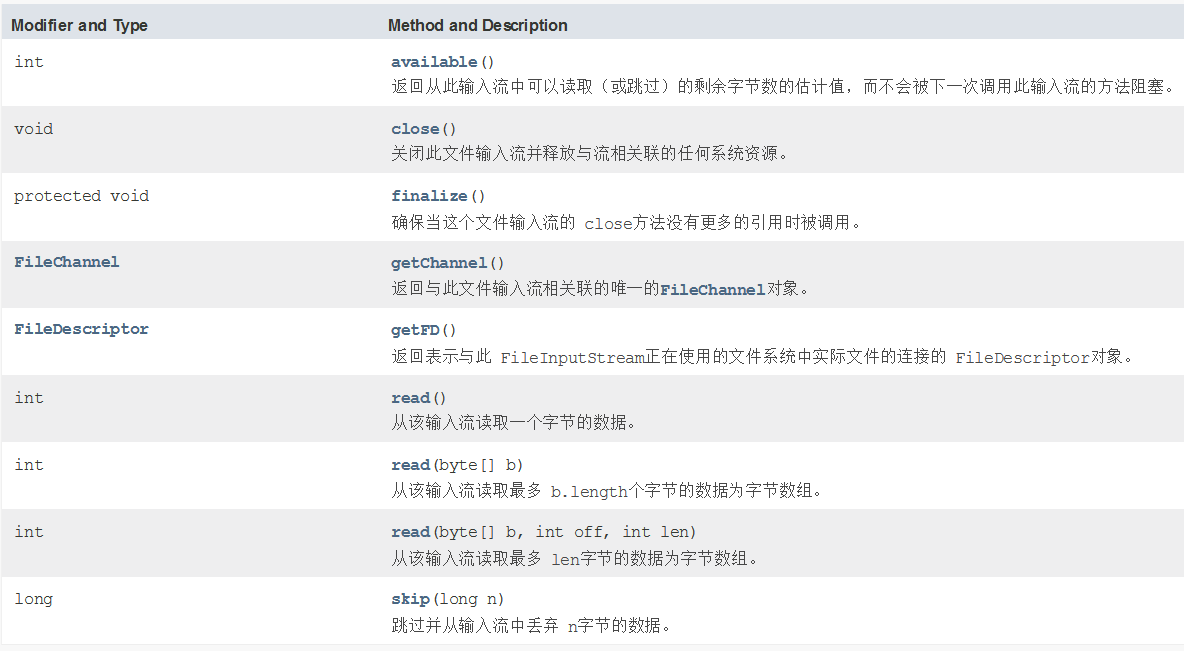
输入流的唯一目的是提供通往数据的通道,程序可以通过这个通道读取文件中的数据。
read方法提供了一个从输入流读取数据的基本方法,read方法的格式如下:
| 返回值 | 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| int | read( ) | 从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节 |
| int | read(byte[ ] b) | 从输入流中读取一定数量的字节,并将其存储在缓冲区数组 b 中。以整数形式返回读取的字节数。 |
| int | read(byte[ ] b, int off, int len) | 将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入 byte 数组。尝试读取 len 个字节,但读取的字节也可能小于该值。以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。 |
| void | close( ) | 关闭流 |
注:read方法在从输入流中读取源中的数据时,如果到达源的末尾,便会返回-1。
FileInputStream流顺序地读取文件,只要不关闭流,每次调用read方法就顺序的读取源中其余的内容,直至源的末尾或流被关闭。
例子:
package li.io.inputstream_;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
//演示FileInputStream的使用(字节输入流 文件-->程序)
public class FileInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 演示读取文件
* read():单个字节的读取,效率较低
*/
@Test
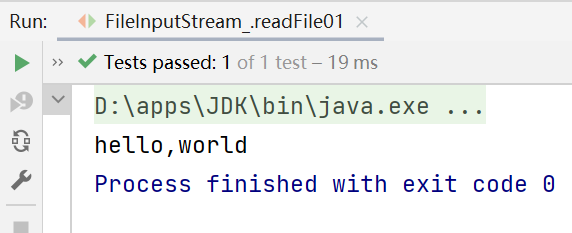
public void readFile01() {
String filePath = "d:\hello.txt";
int readData = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建了FileInputStream对象,用于读取文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//read()方法:从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 如果没有输入可用,此方法将阻止。
//如果返回-1,则表示达到文件的末尾,表示读取完毕
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) readData);//转成char显示,因此如果文件里面有中文字符(每个中文字符占三个字节),显示的时候就会出现乱码
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭文件流,释放资源
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 使用read(byte[] b)读取文件,提高效率
*/
@Test
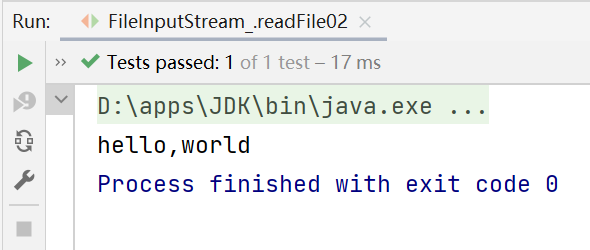
public void readFile02() {
String filePath = "d:\hello.txt";
//字节数组
byte[] buf = new byte[8];//一次读取8个字节
int readLen = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建了FileInputStream对象,用于读取文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//read(byte[] b)方法:从该输入流读取最多b.length字节的数据到字节数组。
//如果返回-1,则表示达到文件的末尾,表示读取完毕
//如果读取正常,返回实际读取的字节数
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen));//显示
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭文件流,释放资源
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
4.2文件字节输出流-FileOutputStream

常用方法:

例子:FileOutputStream应用实例1
要求:请使用FileOutputStream在a.txt文件中写入“hello,world”。如果文件不存在,就先创建文件。
(注意:前提是目录已经存在)
package li.io.outputstream_;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileOutputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 演示使用FileOutputStream将数据写到文件中,如果该文件不存在,则先创建文件
*/
@Test
public void writeFile() {
String filePath = "d:\a.txt";
//创建FileOutputStream对象
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
//得到一个FileOutputStream对象
/*
如果是以new FileOutputStream(filePath)的方式创建对象,
则当写入内容时,会覆盖原来的内容
如果是以new FileOutputStream(filePath,true)的方式创建对象,
则当写入内容时,是在旧内容的末尾追加新内容
*/
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath,true);//以追加的形式去添加新内容
//写入一个字节
//fileOutputStream.write("H");
//写入字符串
String str = "Hello,Jack!";
//String的getBytes方法可以将字符串转为字符数组
// fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());
/*
write(byte[] b,int off,int len)
将len长度的字节从位于偏移量off的指定字节输入写入此文件输出流
*/
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), 0, 4);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
追加前: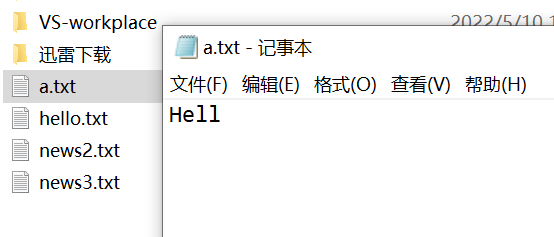
追加后: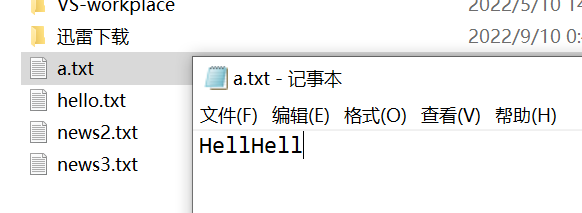
4.2.1FileInputStream&&FileOutputStream
应用实例2:文件拷贝
要求:完成文件拷贝,将d:Koala.png拷贝到d:Koala222.png
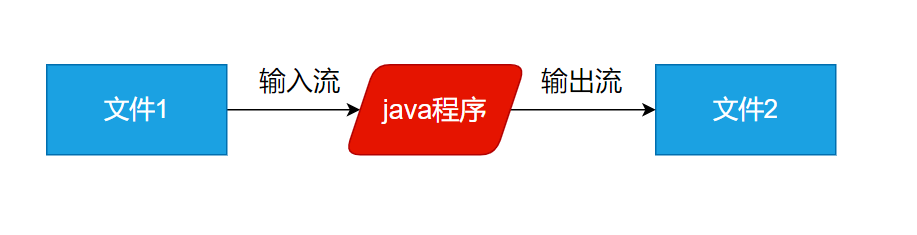
在完成程序时,为防止读取的文件过大,应该是每读取部分数据,就写入到指定文件,这里使用循环。
package li.io.outputstream_;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//完成文件拷贝,将c:\Koala.png拷贝到d:\
/*
思路分析:
1.创建文件的输入流,将文件读入到程序
2.创建文件的输出流,将读取到的文件数据写入指定的文件
*/
String srcFilePath = "d:\Koala.png";
String destFilePath = "d:\Koala222.png";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath, true);
//定义一个字节数组,提高效率
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];//1K
int readLen = 0;
while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {
//读取到后,就通过 fileOutputStream写入到文件
//即,是一边读一边写)
fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, readLen);//一定要使用这个方法
}
System.out.println("拷贝成功~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭输入流和输出流,释放资源
try {
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
4.3文件字符流FileReader&FileWriter
FileReader和FileWriter介绍:
FileReader和FileWriter是字符流,即按照字符来操作io
-
FileReader相关方法:
- new FileReader(String/File)
- read:每次读取单个字符,返回该字符,如果到文件末尾返回-1
- read(char[]):批量读取多个字符到数组,返回读取到的字符数,如果到文件末尾就返回-1
相关API:
- new String(char[]):将char[]转换成String
- new String(char[],off,len):将char[]的制定部分转换成String
-
FileWriter常用方法:
- new FileWriter(File/String):覆盖模式,相当于流的指针在首端
- new FileWriter(File/String,true):追加模式,相当于流的指针在尾端
- writer(int):写入单个字符
- writer(char[]):写入指定数组
- writer(char[],off,len):写入指定数组的指定部分
- writer(String):写入整个字符串
- writer(String,off,len):写入指定字符串的指定部分
相关API:String类:toCharArray:将String转换成char[]
注意:FileWriter使用后,必须要关闭(close)或刷新(flush),否则写入不到指定的文件!