Mybatis 插件使用及源码分析
Mybatis 插件
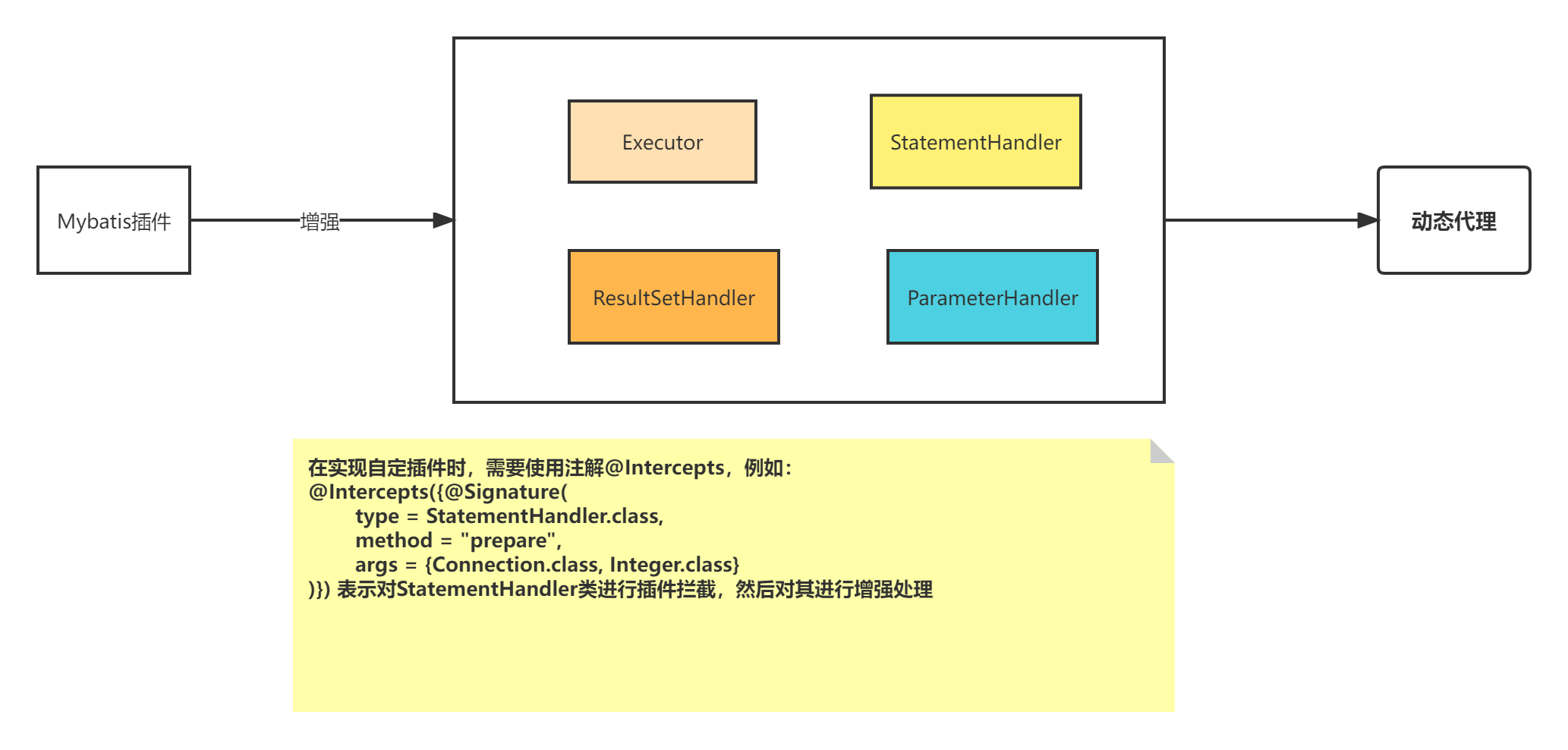
Mybatis插件主要是通过JDK动态代理实现的,插件可以针对接口中的方法进行代理增强,在Mybatis中比较重要的接口如下:
Executor:sql执行器,包含多个实现类,比如SimpleExecutorStatementHander:sql语句处理器,用于将sql语句与Statement的映射,实现类有:PrepareStatementHandler、SimpleStatementHandler、CallBackStatementHandlerParameterHandler:用于参数处理,将传入的参数一一的解析并将类型解析出来,会用到TypeHandler,最终这些数据会用于StatementHandler进行数据的映射,比如?对应的值的映射ResultSetHandler:结果值的处理器,用于数据在查询出来之后,将数据通过ResultSet把数据映射给返回值类型的类上,通过反射(内省)处理映射数据
Mybatis插件的使用
Mybatis插件使用通过@Intercepts注解进行接口的绑定,如下定义一个插件类
/**
* @author <a href="2360564660@qq.com">redwinter</a>
* @since 1.0
**/
@Intercepts({@Signature(
type = StatementHandler.class,
method = "prepare",
args = {Connection.class, Integer.class}
)})
@Slf4j
public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
log.info("对方法进行增强....");
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
log.info("获取属性值:{}", properties);
}
}
然后需要将定义的插件配置mybatis的配置文件中:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 引用db.properties配置文件 -->
<properties resource="db.properties"/>
<!--在 MyBatis 配置文件 mybatis-config.xml 里面添加一项 setting 来选择其它日志实现,
可选的值有:SLF4J、LOG4J、LOG4J2、JDK_LOGGING、COMMONS_LOGGING、STDOUT_LOGGING、NO_LOGGING,
或者是实现了 org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log 接口,且构造方法以字符串为参数的类完全限定名。-->
<settings>
<!-- 打印sql日志 -->
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING" />
<!--开启二级缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.redwinter.study.mybatis.model"/>
</typeAliases>
<!--mybatis插件的配置 -->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="mybatis.plugins.MyPlugin">
<property name="redwinter" value="冬玲"/>
</plugin>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<!--不能配置方言,配置后分页失效-->
<!-- <property name="dialect" value="com.github.pagehelper.dialect.rowbounds.MySqlRowBoundsDialect"/>-->
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!--
development : 开发模式
work : 工作模式
-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 配置数据库连接信息 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- value属性值引用db.properties配置文件中配置的值 -->
<property name="driver" value="${driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${url}" />
<property name="username" value="${name}" />
<property name="password" value="${password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!-- <mapper resource="mappers/UserMapper.xml"/>-->
<package name="mybatis.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
这样就可以生效了,当我们执行数据查询的时候,只要是执行了StatementHandler#prepare方法,那么都会执行到自定的逻辑增强
日志如下:
Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@1386958]
16:02:38.260 [main] INFO mybatis.plugins.MyPlugin - 对方法进行增强....
==> Preparing: update user set name = ?, age = ? where id = ?
==> Parameters: 李四(String), 19(Integer), 1(Integer)
<== Updates: 1
Committing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@1386958]
Cache Hit Ratio [mybatis.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.5
16:02:38.303 [main] INFO mybatis.plugins.MyPlugin - 对方法进行增强....
==> Preparing: select * from user where id = ?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, age, name
<== Row: 1, 19, 李四
<== Total: 1
false
源码分析
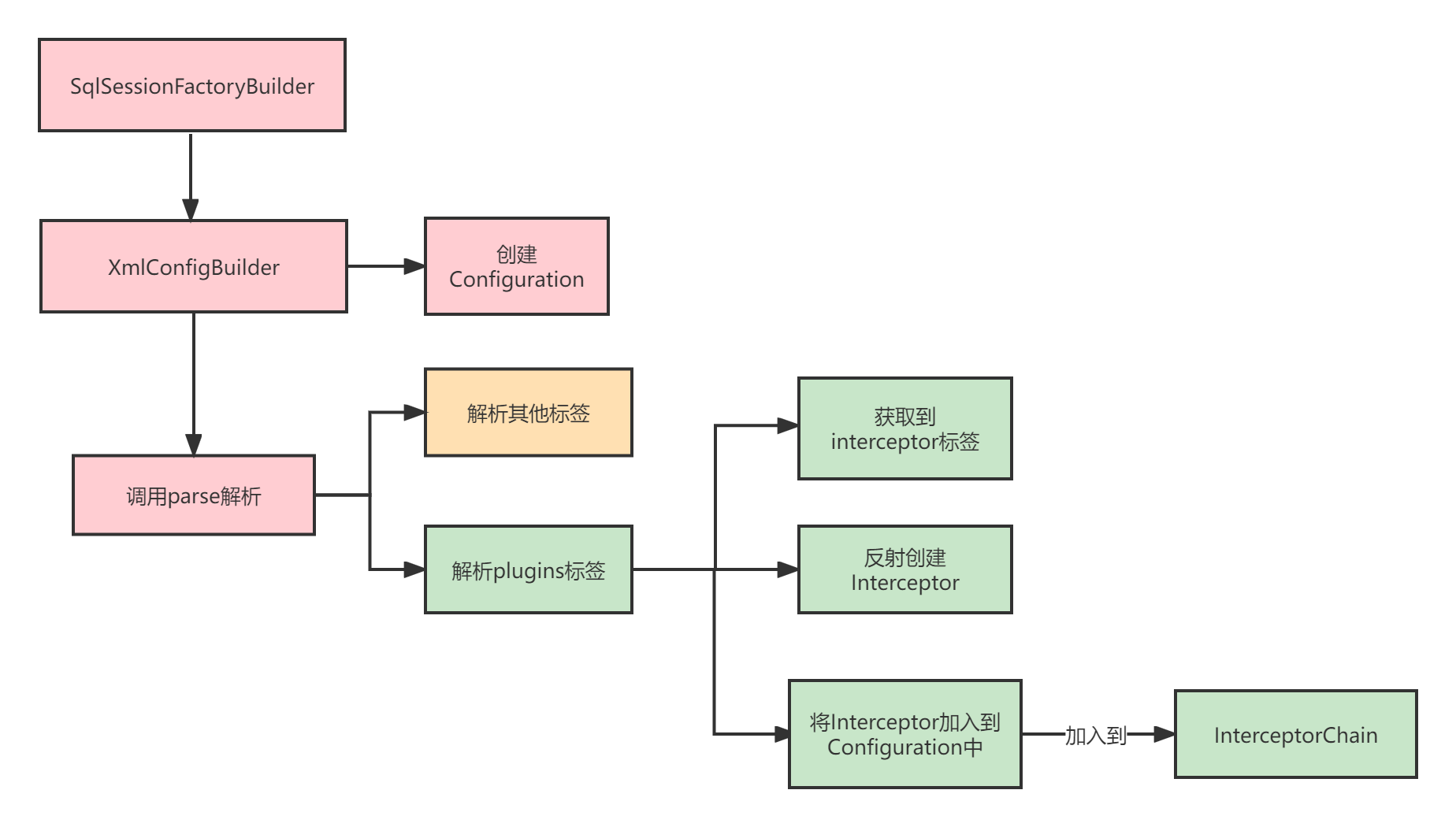
首先我们自定义的插件,需要配置到xml文件中,然后在启动程序的时候,会先创建SqlSession,那么在之前需要进行xml的解析,在Mybatis中解析时通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建一个SqlSessionFactory,然后在通过SqlSessionFactory创建一个SqlSession。在这个过程中,SqlSesssionFactoryBuilder会去创建一个XmlConfigBuilder去解析Xml配置,在XmlConfigBuilder的构造函数中会创建Configuration类,这个类中保存了Mybatis的所有配置。
然后XmlConfigBuilder调用parse方法开始解析配置,解析时会根据xml中的配置一一解析,并且解析是有顺序的以来,解析的顺序是:
properties用于配置外部资源的属性配置,比如配置jdbc的配置文件用于下面的环境信息配置settings用于设置Mybatis内置的设置,比如日志、缓存等,这些配置其实都是Configuration类中的setter方法的配置,Mybatis使用反射(内省)将Configuration的属性通过Properties对象key-value一一进行了对应。typeAliases用于配置别名的配置,在Mybatis中默认了很多的别名,比如Java的基本数据类型,常用了的集合对象,日期对象等都进行了提前的别名配置,这些配置都会注册到TypeAliasRegistry的一个Map中。plugins用于插件的配置,比如自定义的插件,Mybatis的插件是通过JDK动态代理进行增强操作的,Mybatis提供了Interceptor接口,最终会将这些接口全部加载Interceptor加入到InterceptorChain中的List集合中。objectFactory、objectWrapperFactory、reflectorFactory这些不怎么常用enviroments用于配置环境信息的,比如JDBC数据源的信息,这个配置可以配置多个环境,比如开发环境,生产环境等databaseIdProvider这个也不常用typeHandlers类型处理器的配置mappers用于配置Mapper.xml的配置或者Mapper接口的配置,可以配置包路径,xml的路径资源
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build方法:
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
// 创建一个解析xml的构建器,构造函数中会创建一个Configuration类
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
// 解析xml配置
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
创建XMLConfiBuilder类
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}
创建Configuration类
public Configuration() {
// 添加别名
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SOFT", SoftCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("WEAK", WeakCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("XML", XMLLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("RAW", RawLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SLF4J", Slf4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("COMMONS_LOGGING", JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J", Log4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J2", Log4j2Impl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDK_LOGGING", Jdk14LoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("STDOUT_LOGGING", StdOutImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("NO_LOGGING", NoLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("CGLIB", CglibProxyFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JAVASSIST", JavassistProxyFactory.class);
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);
languageRegistry.register(RawLanguageDriver.class);
}
创建TypeAliasRegistry类
private final Map<String, Class<?>> typeAliases = new HashMap<>();
public TypeAliasRegistry() {
// 注册别名,最终全部会注册到Map中
registerAlias("string", String.class);
registerAlias("byte", Byte.class);
registerAlias("char", Character.class);
registerAlias("character", Character.class);
registerAlias("long", Long.class);
registerAlias("short", Short.class);
registerAlias("int", Integer.class);
registerAlias("integer", Integer.class);
registerAlias("double", Double.class);
registerAlias("float", Float.class);
registerAlias("boolean", Boolean.class);
registerAlias("byte[]", Byte[].class);
registerAlias("char[]", Character[].class);
registerAlias("character[]", Character[].class);
registerAlias("long[]", Long[].class);
registerAlias("short[]", Short[].class);
registerAlias("int[]", Integer[].class);
registerAlias("integer[]", Integer[].class);
registerAlias("double[]", Double[].class);
registerAlias("float[]", Float[].class);
registerAlias("boolean[]", Boolean[].class);
registerAlias("_byte", byte.class);
registerAlias("_char", char.class);
registerAlias("_character", char.class);
registerAlias("_long", long.class);
registerAlias("_short", short.class);
registerAlias("_int", int.class);
registerAlias("_integer", int.class);
registerAlias("_double", double.class);
registerAlias("_float", float.class);
registerAlias("_boolean", boolean.class);
registerAlias("_byte[]", byte[].class);
registerAlias("_char[]", char[].class);
registerAlias("_character[]", char[].class);
registerAlias("_long[]", long[].class);
registerAlias("_short[]", short[].class);
registerAlias("_int[]", int[].class);
registerAlias("_integer[]", int[].class);
registerAlias("_double[]", double[].class);
registerAlias("_float[]", float[].class);
registerAlias("_boolean[]", boolean[].class);
registerAlias("date", Date.class);
registerAlias("decimal", BigDecimal.class);
registerAlias("bigdecimal", BigDecimal.class);
registerAlias("biginteger", BigInteger.class);
registerAlias("object", Object.class);
registerAlias("date[]", Date[].class);
registerAlias("decimal[]", BigDecimal[].class);
registerAlias("bigdecimal[]", BigDecimal[].class);
registerAlias("biginteger[]", BigInteger[].class);
registerAlias("object[]", Object[].class);
registerAlias("map", Map.class);
registerAlias("hashmap", HashMap.class);
registerAlias("list", List.class);
registerAlias("arraylist", ArrayList.class);
registerAlias("collection", Collection.class);
registerAlias("iterator", Iterator.class);
registerAlias("ResultSet", ResultSet.class);
}
调用XMLConfigBuilder#parse方法
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// 解析配置,从根的configuration的标签开始
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
// 加载自定义的日志打印
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
// 解析别名
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
// 添加插件
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
// 设置默认的配置
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
// 解析环境信息
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
// 解析类型处理器标签
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 解析mappers标签
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
解析插件标签:
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
// 将插件全部加入到配置中,最终会加载到InterceptorChain类的List集合中
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
当我们调用方法执行Sql的时候,Mybatis会通过SqlSession去委派调用Executor的接口的方法进行执行。比如我们调用selectList(statementId) 去执行查询,那么会调用:
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
// 获取Mapper中解析的配置,这个类中存放了sql语句,返回类型,参数类型等
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
调用query方法就会委派到Executor接口的实现类BaseExecutor类中进行执行:
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取sql语句,解析出sql语句,参数类型,参数值等数据
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 创建一个缓存key,用于缓存存储使用
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
调用query重载方法:如果缓存中有,那么就从缓存中获取,如果没有那么执行数据库查询
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 从缓存中获取数据
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 查询数据从数据库
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
最终会中到SimpleExecutor实现类的doQuery方法去真正执行查询:
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 获取配置
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建一个StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
在调用newStatementHandler方法是会执行到插件的pluginAll方法,执行动态代理的创建代理对象:
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 这里拿到的是一个代理对象
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
拦截器链去调用pluginAll,然后调用Interceptor的plugin方法创建代理对象:
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
// 遍历所有的插件,然后执行plugin方法,获取到代理的对象
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
// Interceptor的默认接口方法plugin
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
// Plugin类中的包装创建一个代理对象
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 获取类和方法集合
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 目标的接口,代理生成的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
// 创建一个jdk动态代理
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
这样的话就完成了拦截器插件的代理对象的创建,这里创建出来的代理对象就是StatementHandler,在前面自定义的插件,配置的是拦截StatementHandler#prepare方法,那么在哪里执行的呢?
回到Executor接口实现类SimpleExecutor了中doQuery方法,这个方法中会去创建一个预编译SQL处理器,执行prepareStatement方法:
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获取一个数据库连接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 获取Statement 这里可能获取到PrepareStatement 、SimpleStatement、CallbackStatement
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 设置参数
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
这里的话就会调用prepare方法,这个方法就是自定义插件配置需要拦截的方法,由于这个handler是一个代理对象,我们都知道只要是代理对象,只要执行代理对象的任何方法都会去执行InvoketionHandler接口的invoke方法,当执行到这个方法的时候就会调用到我们自定义的插件类中intercept方法:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
// 如果拦截的方法与执行的方法一致那么执行intercept方法进行增加强
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
// 如果不是则执行方法即可
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
所以只要我们执行了sql查询,那么都会通过JDK动态代理创建的代理对象去执行到这个增强方法。
插件的扩展
在Mybatis中有个分页的插件叫PageHelper,这个插件就是使用了Mybatis插件机制完成的,当然还有比如早期的TkMapper插件。接下来分析一下PageHelper是如何实现分页机制的。
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.3.0</version>
</dependency>
然后在mybatis-config.xml配置文件中配置插件让分页插件生效:
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="mybatis.plugins.MyPlugin">
<property name="redwinter" value="冬玲"/>
</plugin>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<!--不能配置方言,配置后分页失效-->
<!-- <property name="dialect" value="com.github.pagehelper.dialect.rowbounds.MySqlRowBoundsDialect"/>-->
</plugin>
</plugins>
然后就可以直接使用了:
@Test
public void testPageHelper() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 设置分页参数
PageHelper.startPage(1, 2);
List<User> users = mapper.selectAll();
// 构建分页信息
PageInfo<User> pageInfo = new PageInfo<User>(users);
System.out.println(pageInfo);
}
日志如下:
Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@14a2528]
11:06:43.511 [main] INFO mybatis.plugins.MyPlugin - 对方法进行增强....
==> Preparing: SELECT count(0) FROM user
==> Parameters:
<== Columns: count(0)
<== Row: 3
<== Total: 1
Cache Hit Ratio [mybatis.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.0
11:06:43.562 [main] INFO mybatis.plugins.MyPlugin - 对方法进行增强....
==> Preparing: select * from user LIMIT ?
==> Parameters: 2(Integer)
<== Columns: id, age, name
<== Row: 1, 19, 李四
<== Row: 2, null, 里斯
<== Total: 2
PageInfo{pageNum=1, pageSize=2, size=2, startRow=1, endRow=2, total=3, pages=2, list=Page{count=true, pageNum=1, pageSize=2, startRow=0, endRow=2, total=3, pages=2, reasonable=false, pageSizeZero=false}[User(id=1, age=19, name=李四), User(id=2, age=0, name=里斯)], prePage=0, nextPage=2, isFirstPage=true, isLastPage=false, hasPreviousPage=false, hasNextPage=true, navigatePages=8, navigateFirstPage=1, navigateLastPage=2, navigatepageNums=[1, 2]}
可以看到这里执行了两条sql语句,一个是查询总条数,一个是分页查询,那PageHelper怎么实现的呢?
PageHelper 分页源码解析
由于我们在mybatis-config.xml中配置了分页插件,那么直接进PageInterceptor这个类去看看,找到intercept方法:
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
try {
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0];
Object parameter = args[1];
RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2];
ResultHandler resultHandler = (ResultHandler) args[3];
Executor executor = (Executor) invocation.getTarget();
CacheKey cacheKey;
BoundSql boundSql;
//由于逻辑关系,只会进入一次
if (args.length == 4) {
//4 个参数时
boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
cacheKey = executor.createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
} else {
//6 个参数时
cacheKey = (CacheKey) args[4];
boundSql = (BoundSql) args[5];
}
checkDialectExists();
//对 boundSql 的拦截处理
if (dialect instanceof BoundSqlInterceptor.Chain) {
boundSql = ((BoundSqlInterceptor.Chain) dialect).doBoundSql(BoundSqlInterceptor.Type.ORIGINAL, boundSql, cacheKey);
}
List resultList;
//调用方法判断是否需要进行分页,如果不需要,直接返回结果
if (!dialect.skip(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) {
//判断是否需要进行 count 查询
if (dialect.beforeCount(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) {
//查询总数
Long count = count(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql);
//处理查询总数,返回 true 时继续分页查询,false 时直接返回
if (!dialect.afterCount(count, parameter, rowBounds)) {
//当查询总数为 0 时,直接返回空的结果
return dialect.afterPage(new ArrayList(), parameter, rowBounds);
}
}
resultList = ExecutorUtil.pageQuery(dialect, executor,
ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql, cacheKey);
} else {
//rowBounds用参数值,不使用分页插件处理时,仍然支持默认的内存分页
resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, cacheKey, boundSql);
}
return dialect.afterPage(resultList, parameter, rowBounds);
} finally {
if(dialect != null){
dialect.afterAll();
}
}
}
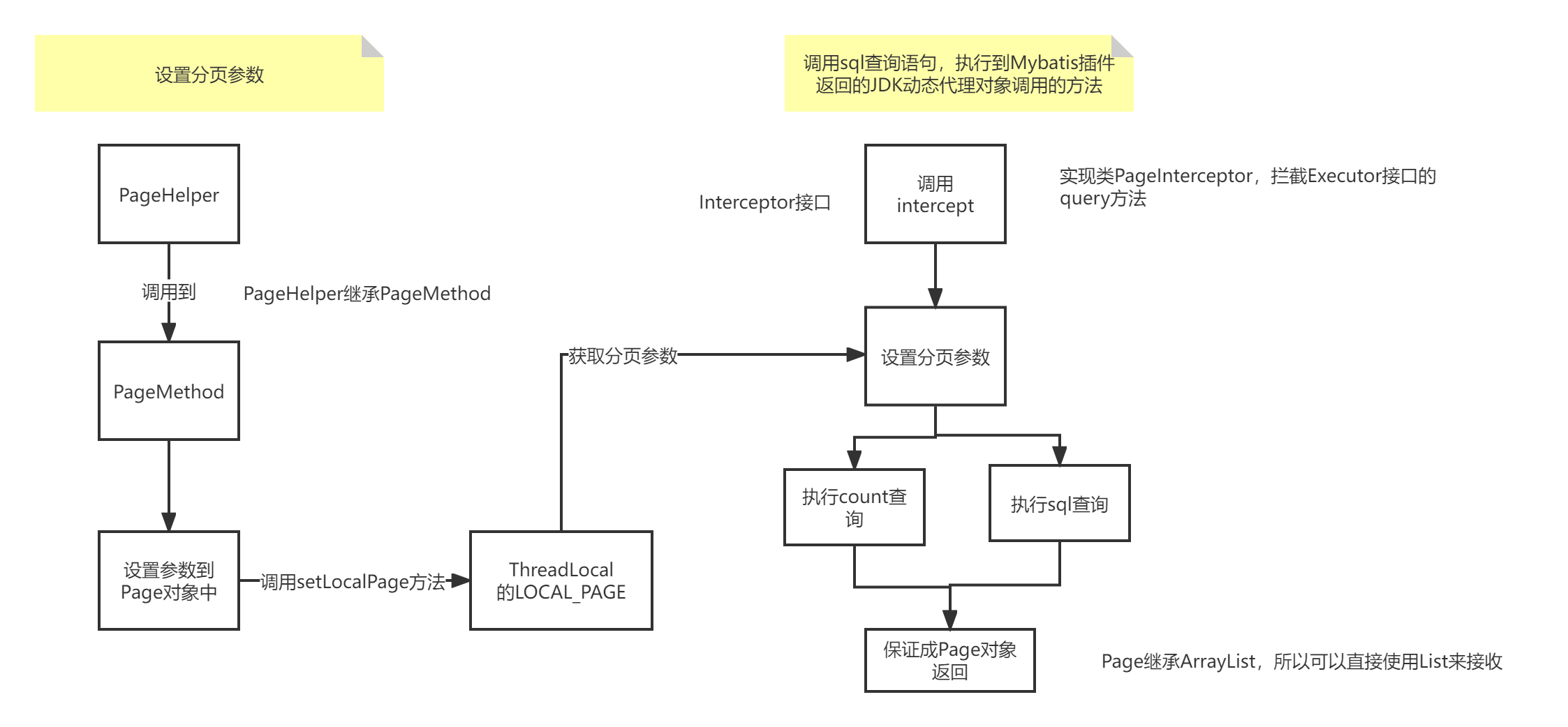
根据Debug发现这返回的对象实际上是一个Page对象,这个对象继承ArrayList,所以在查询多个数据时可以直接通过List集合获取,最终在分装到PageInfo对象中就完成了分页数据的封装。那么这些分页数据是何时设置进去的呢?
实际上在进行PageHelper.startPage(1, 2);时,这个参数设置在ThreadLocal中,在PageMethod类中:
/**
* 开始分页
*
* @param pageNum 页码
* @param pageSize 每页显示数量
* @param count 是否进行count查询
* @param reasonable 分页合理化,null时用默认配置
* @param pageSizeZero true且pageSize=0时返回全部结果,false时分页,null时用默认配置
*/
public static <E> Page<E> startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize, boolean count, Boolean reasonable, Boolean pageSizeZero) {
Page<E> page = new Page<E>(pageNum, pageSize, count);
page.setReasonable(reasonable);
page.setPageSizeZero(pageSizeZero);
//当已经执行过orderBy的时候
Page<E> oldPage = getLocalPage();
if (oldPage != null && oldPage.isOrderByOnly()) {
page.setOrderBy(oldPage.getOrderBy());
}
setLocalPage(page);
return page;
}
调用setLocalPage方法就会设置到ThreadLocal中:
protected static final ThreadLocal<Page> LOCAL_PAGE = new ThreadLocal<Page>();
protected static boolean DEFAULT_COUNT = true;
/**
* 设置 Page 参数
*
* @param page
*/
protected static void setLocalPage(Page page) {
LOCAL_PAGE.set(page);
}
在执行查询的到时候会调用到getLocalPage方法获取ThreadLocal中的参数,然后设置到分页参数中并构建出sql语句用于分页查询,在执行完之后会在finally中调用clearPage清除掉ThreadLoacl中的数据。