springmvc异常处理解析#ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
开头
试想一下我们一般怎么统一处理异常呢,答:切面。但抛开切面不讲,如果对每一个controller方法抛出的异常做专门处理,那么着实太费劲了,有没有更好的方法呢?当然有,就是本篇文章接下来要介绍的springmvc的异常处理机制,用到了ControllerAdvice和ExceptionHandler注解,有点切面的感觉哈哈。
1.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
首先从springmvc的异常处理解析器开始讲,当执行完controller方法后,不管有没有异常产生都会调用DispatcherServlet#doDispatch()方法中的processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); 方法,接着会判断是否有异常,若无异常则走正常流程,若有异常则需要进行处理 mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); 再接着就是遍历spring已经注册的异常处理解析器直到有处理器返回mav
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
// 执行处理器产生的异常处理
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
// 是否有异常视图返回
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render? 处理程序是否返回要渲染的视图
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
// 渲染视图
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name "" + getServletName() +
"": assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
}
} @Nullable
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
// Check registered HandlerExceptionResolvers...
ModelAndView exMv = null;
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) {
for (HandlerExceptionResolver handlerExceptionResolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) {
exMv = handlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (exMv != null) {
break;
}
}
}
if (exMv != null) {
// 无视图view
if (exMv.isEmpty()) {
request.setAttribute(EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
return null;
}
// We might still need view name translation for a plain error model...
if (!exMv.hasView()) {
String defaultViewName = getDefaultViewName(request);
if (defaultViewName != null) {
exMv.setViewName(defaultViewName);
}
}
WebUtils.exposeErrorRequestAttributes(request, ex, getServletName());
return exMv;
}
throw ex;
}
其中最重要也是最常使用的一个处理器就是ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,下面将着重介绍它,先来看看这个类的继承结构图,实现了InitializingBean接口,在这个bean创建完成之前会调用生命周期初始化方法afterPropertiesSet(),这里面包含了对@ControllerAdvice注解的解析,初始化完后的信息供后续解析异常使用。
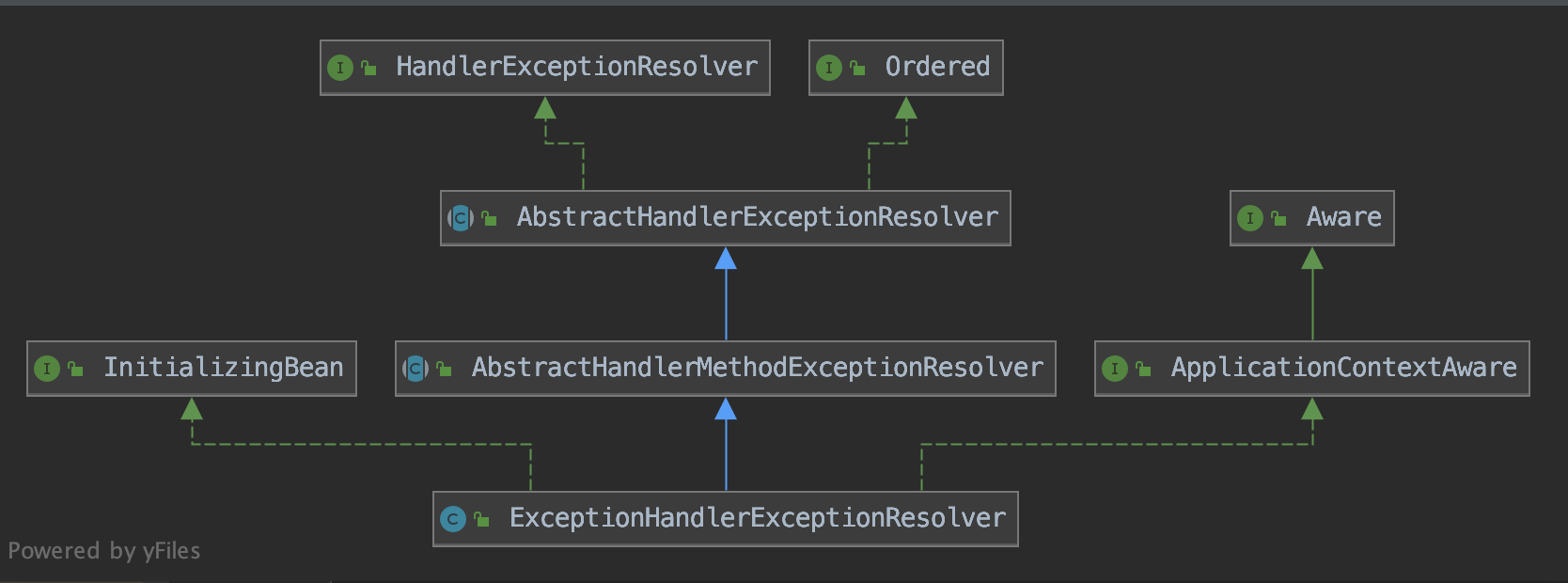
实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口,实现解析方法resolveException()
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver {
/**
* Try to resolve the given exception that got thrown during handler execution,
* returning a {@link ModelAndView} that represents a specific error page if appropriate.
* <p>The returned {@code ModelAndView} may be {@linkplain ModelAndView#isEmpty() empty}
* to indicate that the exception has been resolved successfully but that no view
* should be rendered, for instance by setting a status code.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler the executed handler, or {@code null} if none chosen at the
* time of the exception (for example, if multipart resolution failed)
* @param ex the exception that got thrown during handler execution
* @return a corresponding {@code ModelAndView} to forward to,
* or {@code null} for default processing in the resolution chain
*/
@Nullable
ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex);
}@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// Do this first, it may add ResponseBodyAdvice beans
// 初始化异常注解 @ControllerAdvice
initExceptionHandlerAdviceCache();
}
private void initExceptionHandlerAdviceCache() {
if (getApplicationContext() == null) {
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for exception mappings: " + getApplicationContext());
}
// 解析有@ControllerAdvice注解的bean,并将这个bean构建成ControllerAdviceBean对象
List<ControllerAdviceBean> adviceBeans = ControllerAdviceBean.findAnnotatedBeans(getApplicationContext());
// 将ControllerAdviceBean根据order排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(adviceBeans);
for (ControllerAdviceBean adviceBean : adviceBeans) {
Class<?> beanType = adviceBean.getBeanType();
if (beanType == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unresolvable type for ControllerAdviceBean: " + adviceBean);
}
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(beanType);
// mappedMethods 映射不为空
if (resolver.hasExceptionMappings()) {
// 添加到缓存中
this.exceptionHandlerAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, resolver);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected @ExceptionHandler methods in " + adviceBean);
}
}
// 若实现了ResponseBodyAdvice接口(暂不介绍)
if (ResponseBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanType)) {
this.responseBodyAdvice.add(adviceBean);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected ResponseBodyAdvice implementation in " + adviceBean);
}
}
}
} ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(beanType); 这行代码会解析拥有@ControllerAdvice 注解的class,并且会遍历class中带有 @ExceptionHandler 注解的方法,获取方法注解带有的异常类型,将异常类型和方法放入到mappedMethods中供后面获取,获取的时候若对应处理此异常类型的method有多个,则需要进行排序,选取一个异常类型与method ExceptionHandler注解异常类型最近的一个(深度最小的那个也即是继承关系最少的那个)具体代码如下:
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver
public class ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver {
/**
* A filter for selecting {@code @ExceptionHandler} methods.
*/
public static final MethodFilter EXCEPTION_HANDLER_METHODS = method ->
(AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, ExceptionHandler.class) != null);
/**
* 异常类型与方法的映射map
*/
private final Map<Class<? extends Throwable>, Method> mappedMethods = new HashMap<>(16);
/**
* 缓存,用来存储先前碰到过的异常类型与处理方法的映射
*/
private final Map<Class<? extends Throwable>, Method> exceptionLookupCache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(16);
/**
* A constructor that finds {@link ExceptionHandler} methods in the given type.
* @param handlerType the type to introspect
*/
public ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(Class<?> handlerType) {
// 获取并遍历@ExceptionHandler注解的方法
for (Method method : MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, EXCEPTION_HANDLER_METHODS)) {
for (Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType : detectExceptionMappings(method)) {
addExceptionMapping(exceptionType, method);
}
}
}
/**
* Extract exception mappings from the {@code @ExceptionHandler} annotation first,
* and then as a fallback from the method signature itself.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private List<Class<? extends Throwable>> detectExceptionMappings(Method method) {
List<Class<? extends Throwable>> result = new ArrayList<>();
// 将注解ExceptionHandler value值异常添加到result中
detectAnnotationExceptionMappings(method, result);
// 注解值为空的话再去获取参数的异常类型
if (result.isEmpty()) {
for (Class<?> paramType : method.getParameterTypes()) {
if (Throwable.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) {
result.add((Class<? extends Throwable>) paramType);
}
}
}
if (result.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No exception types mapped to " + method);
}
return result;
}
protected void detectAnnotationExceptionMappings(Method method, List<Class<? extends Throwable>> result) {
ExceptionHandler ann = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, ExceptionHandler.class);
Assert.state(ann != null, "No ExceptionHandler annotation");
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(ann.value()));
}
private void addExceptionMapping(Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType, Method method) {
// 将异常类型以及对应的method添加到map中,且异常类型不能有重复否则会报错
Method oldMethod = this.mappedMethods.put(exceptionType, method);
if (oldMethod != null && !oldMethod.equals(method)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous @ExceptionHandler method mapped for [" +
exceptionType + "]: {" + oldMethod + ", " + method + "}");
}
}
/**
* Whether the contained type has any exception mappings.
*/
public boolean hasExceptionMappings() {
return !this.mappedMethods.isEmpty();
}
/**
* Find a {@link Method} to handle the given exception.
* Use {@link ExceptionDepthComparator} if more than one match is found.
* @param exception the exception
* @return a Method to handle the exception, or {@code null} if none found
*/
@Nullable
public Method resolveMethod(Exception exception) {
return resolveMethodByThrowable(exception);
}
/**
* Find a {@link Method} to handle the given Throwable.
* Use {@link ExceptionDepthComparator} if more than one match is found.
* @param exception the exception
* @return a Method to handle the exception, or {@code null} if none found
* @since 5.0
*/
@Nullable
public Method resolveMethodByThrowable(Throwable exception) {
Method method = resolveMethodByExceptionType(exception.getClass());
if (method == null) {
Throwable cause = exception.getCause();
if (cause != null) {
method = resolveMethodByExceptionType(cause.getClass());
}
}
return method;
}
/**
* Find a {@link Method} to handle the given exception type. This can be
* useful if an {@link Exception} instance is not available (e.g. for tools).
* @param exceptionType the exception type
* @return a Method to handle the exception, or {@code null} if none found
*/
@Nullable
public Method resolveMethodByExceptionType(Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType) {
Method method = this.exceptionLookupCache.get(exceptionType);
if (method == null) {
method = getMappedMethod(exceptionType);
this.exceptionLookupCache.put(exceptionType, method);
}
return method;
}
/**
* Return the {@link Method} mapped to the given exception type, or {@code null} if none.
*/
@Nullable
private Method getMappedMethod(Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType) {
List<Class<? extends Throwable>> matches = new ArrayList<>();
for (Class<? extends Throwable> mappedException : this.mappedMethods.keySet()) {
if (mappedException.isAssignableFrom(exceptionType)) {
matches.add(mappedException);
}
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
// exceptionType 到matchs父类异常类型的深度
matches.sort(new ExceptionDepthComparator(exceptionType));
return this.mappedMethods.get(matches.get(0));
}
else {
return null;
}
}
}@Override
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
// exception为controller方法抛出的异常
// 根据异常及其类型从上述的mappedMethods中获取对应的方法,再获取方法所在的对象 封装成ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception);
if (exceptionHandlerMethod == null) {
return null;
}
// 设置参数解析器,主要用来获取方法的参数值的,供后续反射调用方法
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
// 设置返回值解析器,当执行完方法后获取返回值,对返回值进行处理 或返回视图或将结果写入到response
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
try {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking @ExceptionHandler method: " + exceptionHandlerMethod);
}
Throwable cause = exception.getCause();
if (cause != null) {
// Expose cause as provided argument as well
// 执行异常处理方法,也就是我们的自定义的异常处理方法
exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, exception, cause, handlerMethod);
}
else {
// Otherwise, just the given exception as-is
exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, exception, handlerMethod);
}
}
catch (Throwable invocationEx) {
// Any other than the original exception is unintended here,
// probably an accident (e.g. failed assertion or the like).
if (invocationEx != exception && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failed to invoke @ExceptionHandler method: " + exceptionHandlerMethod, invocationEx);
}
// Continue with default processing of the original exception...
return null;
}
// 根据后续的返回值解析器设置的,将返回值写入到response中了直接返回空的mav
if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
return new ModelAndView();
}
else {
ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel();
HttpStatus status = mavContainer.getStatus();
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, status);
mav.setViewName(mavContainer.getViewName());
// (this.view instanceof String)
if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) {
mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView());
}
if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes) {
Map<String, ?> flashAttributes = ((RedirectAttributes) model).getFlashAttributes();
RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes);
}
return mav;
}
}exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, exception, cause, handlerMethod); 此方法执行完成后已经完成了异常处理方法的调用,若方法返回值为视图ModelAndView或其他视图类型,则还需要借助视图解析器如InternalResourceViewResolver对视图进行解析渲染,若为其他类型的值则将值写入到response响应中。
2. demo
Controller类方法:
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "test")
public class HelloWorldController{
@Data
public static class User {
private String username;
private Integer age;
private String address;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "user/get", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public Object testObject(@RequestBody @Valid User user, @RequestParam String address) {
user.setAddress(address);
// 这里特意抛出RuntimeException异常
throw new RuntimeException("this is a exception");
}
}ExceptionHandlerController异常处理类
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class ExceptionHandlerController {
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public Object handleException(Exception e) {
return CommonResult.fail("Exception:" + e.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = RuntimeException.class)
public Object handlerRuntimeException(Exception e) {
return CommonResult.fail("handlerRuntimeException:" + e.getMessage());
}
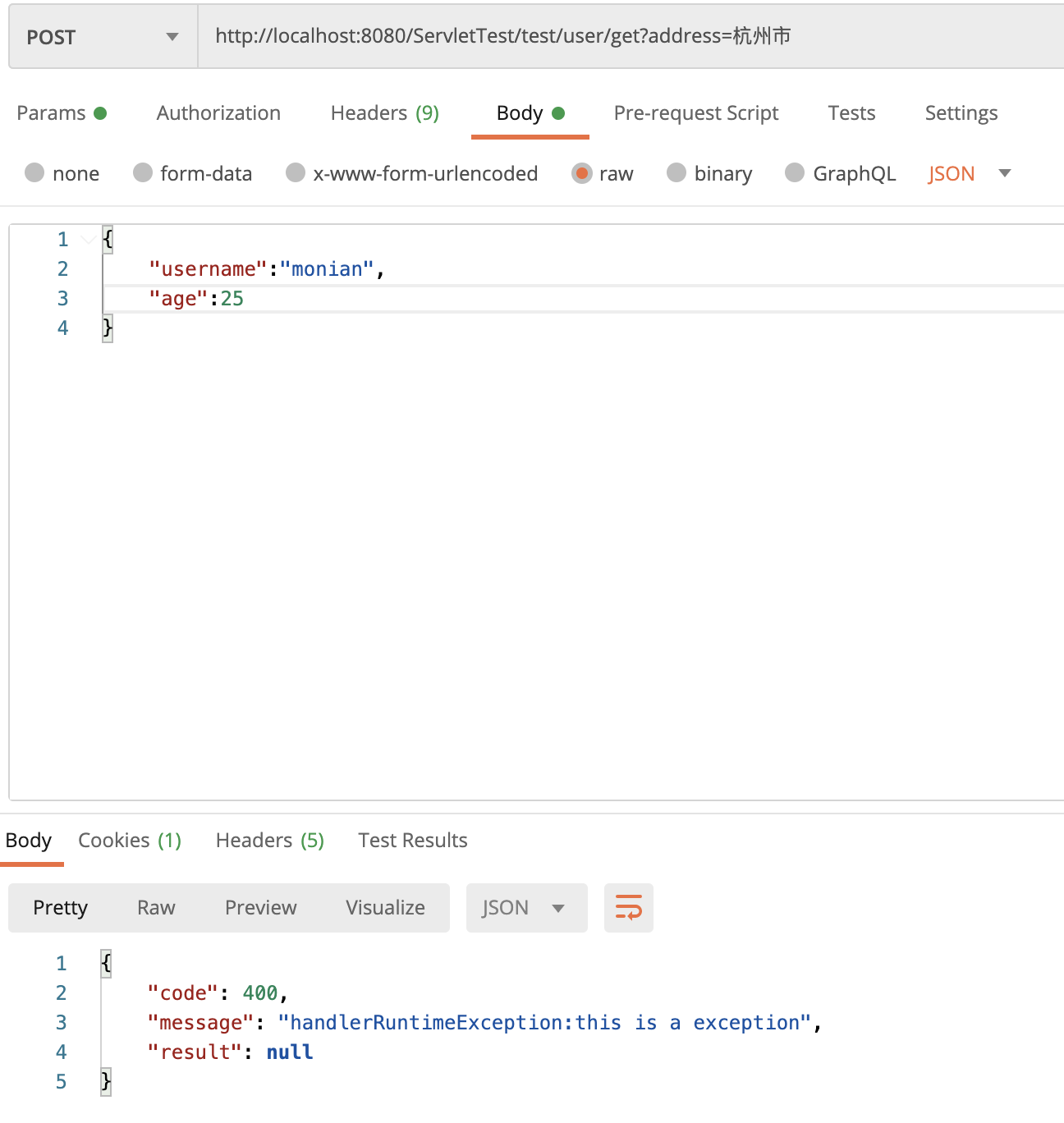
}ExceptionHandlerController类中定义了两个异常处理方法,一个处理Exception异常,一个处理RuntimeException异常,那个根据controller方法抛出的异常RuntimeException再结合上面的分析(RuntimeException到RuntimeException深度为0,RuntimeException到Exception中间继承了一次深度为1)可以得出抛出异常类型的处理方法为handlerRuntimeException 方法。 运行程序结果如下:
结语
初步解析ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver源码,若写的有误或者有不理解的地方,欢迎指出讨论~


